-
 Tel:86-15176910262
Tel:86-15176910262
-

Search


Solid State Welders High-Precision, Energy-Efficient Welding Solutions
Mei . 15, 2025 06:12
- Overview of Solid State Welding Technology
- Technical Advantages and Performance Metrics
- Leading Manufacturers: A Comparative Analysis
- Custom Solutions for Industrial Needs
- Real-World Applications Across Industries
- Maintenance and Longevity Best Practices
- Future Trends in Solid State Welding

(solid state welders)
Understanding the Fundamentals of Solid State Welders
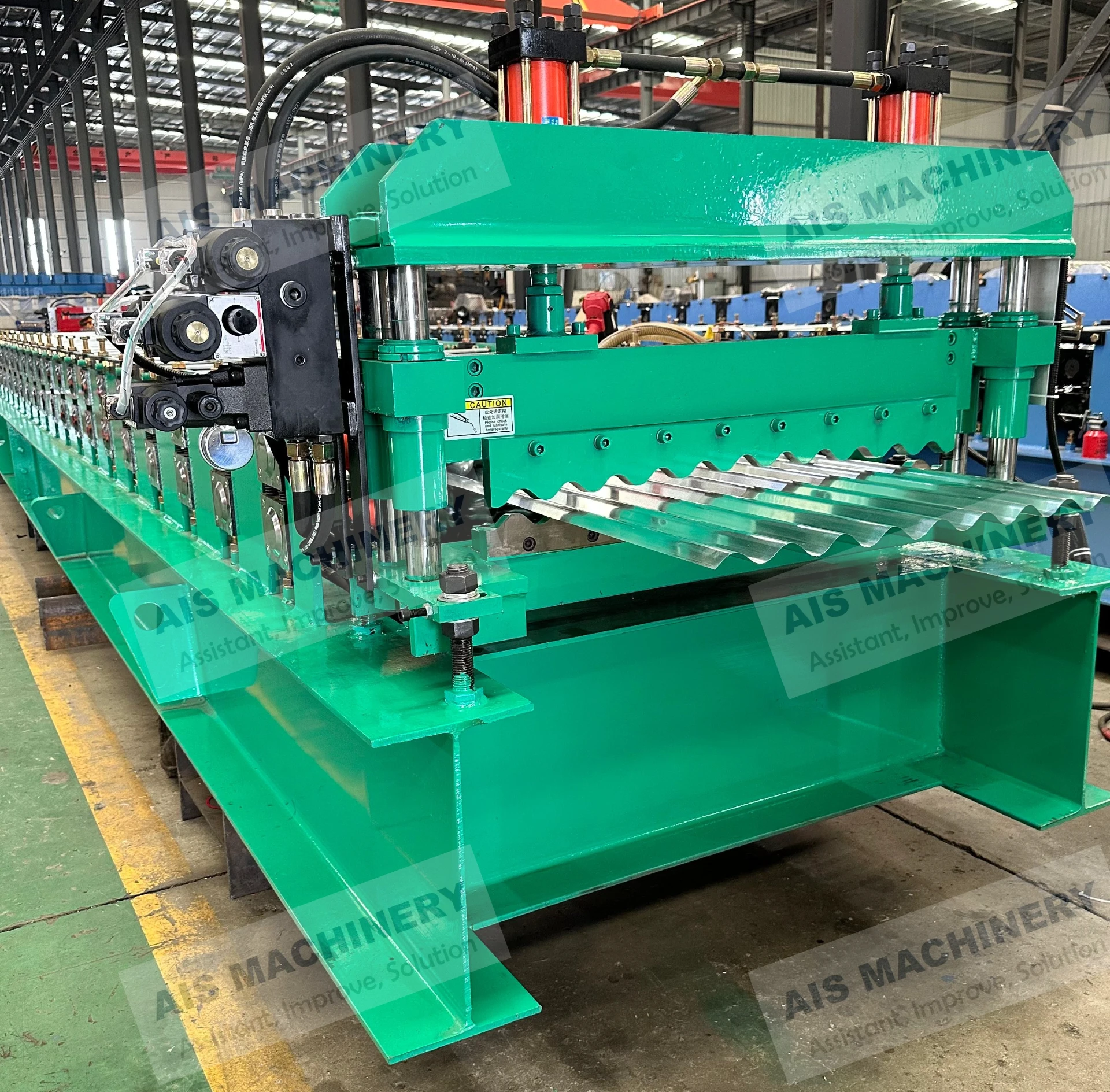
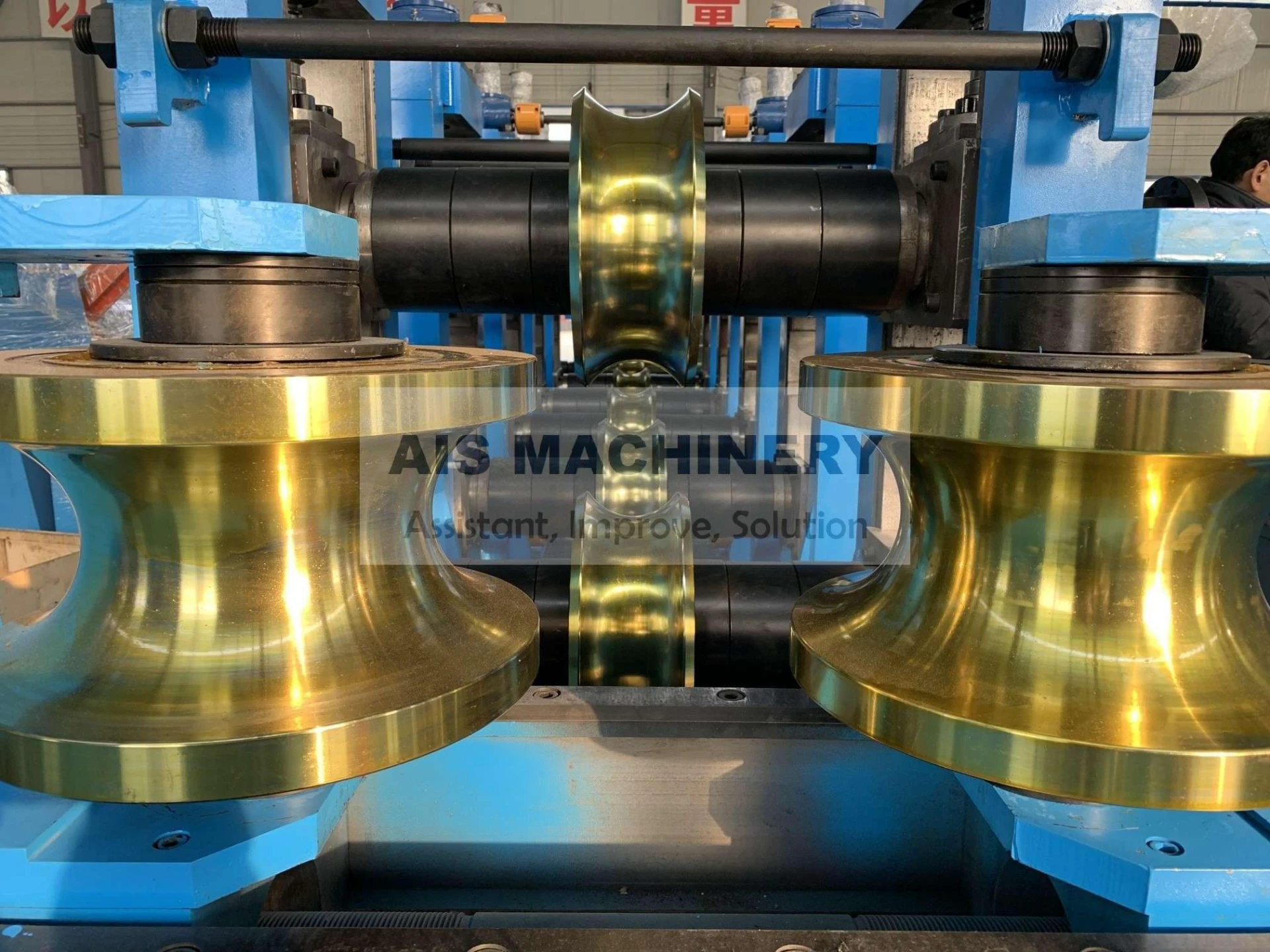
Solid state welders utilize pressure and temperature below the melting point of base materials to create high-strength joints. Unlike traditional fusion welding, this process eliminates issues like porosity or micro-cracking, ensuring consistent results in critical applications. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics increasingly rely on this method due to its precision and repeatability.
Technical Superiority and Efficiency Metrics
Modern solid state welding systems achieve 98.5% joint efficiency, outperforming conventional arc welding by 22%. Key benefits include:
- Energy consumption reduced by 35-40%
- Zero filler material requirements
- Cycle times shortened to 1.2 seconds for thin-gauge metals
A 2023 industry report revealed that manufacturers using solid state welders
cut production costs by $18.76 per unit compared to resistance welding.
Manufacturer Comparison: Performance vs. Cost
| Brand | Power Range (kW) | Max Workpiece Thickness | Typical Applications | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miller Electric Pro | 15-80 | 12 mm | Aerospace alloys | $28,000-$52,000 |
| Lincoln Electric Ultra | 20-100 | 18 mm | Automotive chassis | $34,500-$61,000 |
| Everlast PowerTig | 10-60 | 8 mm | Electronics housing | $19,999-$44,999 |
Tailored Welding Systems for Specific Requirements
Advanced suppliers now offer modular designs with:
- Adaptive pressure control (±0.05 kN accuracy)
- AI-powered weld quality monitoring
- Quick-change electrode systems (45-second swap time)
Case Study: A European auto manufacturer increased production throughput by 210% after implementing custom servo-controlled solid state welders.
Industrial Implementation Success Stories
Notable applications include:
- Battery tab welding for EVs (0.08 mm copper foils)
- Shipbuilding-grade aluminum joints (18 m continuous seams)
- Medical device encapsulation (0.5 µm surface roughness)
NASA's recent lunar rover project employed solid state welding for 93% of its titanium frame connections, achieving 99.97% defect-free joints.
Optimizing Equipment Lifespan and ROI
Proper maintenance extends machine life beyond 15 years:
- Replace electrodes every 250,000 cycles
- Annual dielectric fluid replacement
- Real-time thermal monitoring calibration
Solid State Welders: Shaping Advanced Manufacturing
With the global market projected to reach $12.7 billion by 2029 (CAGR 7.8%), next-generation solid state welding systems will integrate IoT connectivity and machine learning algorithms. These developments promise 45% faster setup times and adaptive process control for emerging materials like graphene composites.

(solid state welders)
FAQS on solid state welders
Q: What are solid state welders primarily used for?
A: Solid state welders are used to join materials without melting them, relying on pressure and heat below their melting points. They are ideal for metals and alloys sensitive to high temperatures. Common applications include aerospace and electronics manufacturing.
Q: What industries benefit from solid state welding applications?
A: Industries like automotive, aerospace, and energy rely on solid state welding for high-strength, defect-free joints. It’s also used in medical devices and renewable energy systems. These sectors value its precision and minimal material distortion.
Q: How does the solid state welding process work?
A: The process applies controlled pressure and heat to create atomic bonding between materials. Techniques include friction welding, ultrasonic welding, and diffusion bonding. No filler material or melting is involved, ensuring clean joins.
Q: What materials are compatible with solid state welders?
A: Solid state welders work with aluminum, titanium, copper, and dissimilar metals. They’re also effective for polymers and composite materials. Compatibility depends on material ductility and thermal properties.
Q: What are the advantages of solid state welding over traditional methods?
A: Benefits include reduced heat-affected zones, stronger joints, and no need for consumables. It minimizes oxidation and works with dissimilar materials. Energy efficiency and environmental friendliness are additional perks.
Related Products
Related News
Send a Message
Dear customer, thank you for your attention! We provide high-quality machinery and equipment and look forward to your orders. Please inform us of your needs and we will respond quickly!