-
 Tel:86-15176910262
Tel:86-15176910262
-

Search


china roll forming machine
Мар . 07, 2025 03:17
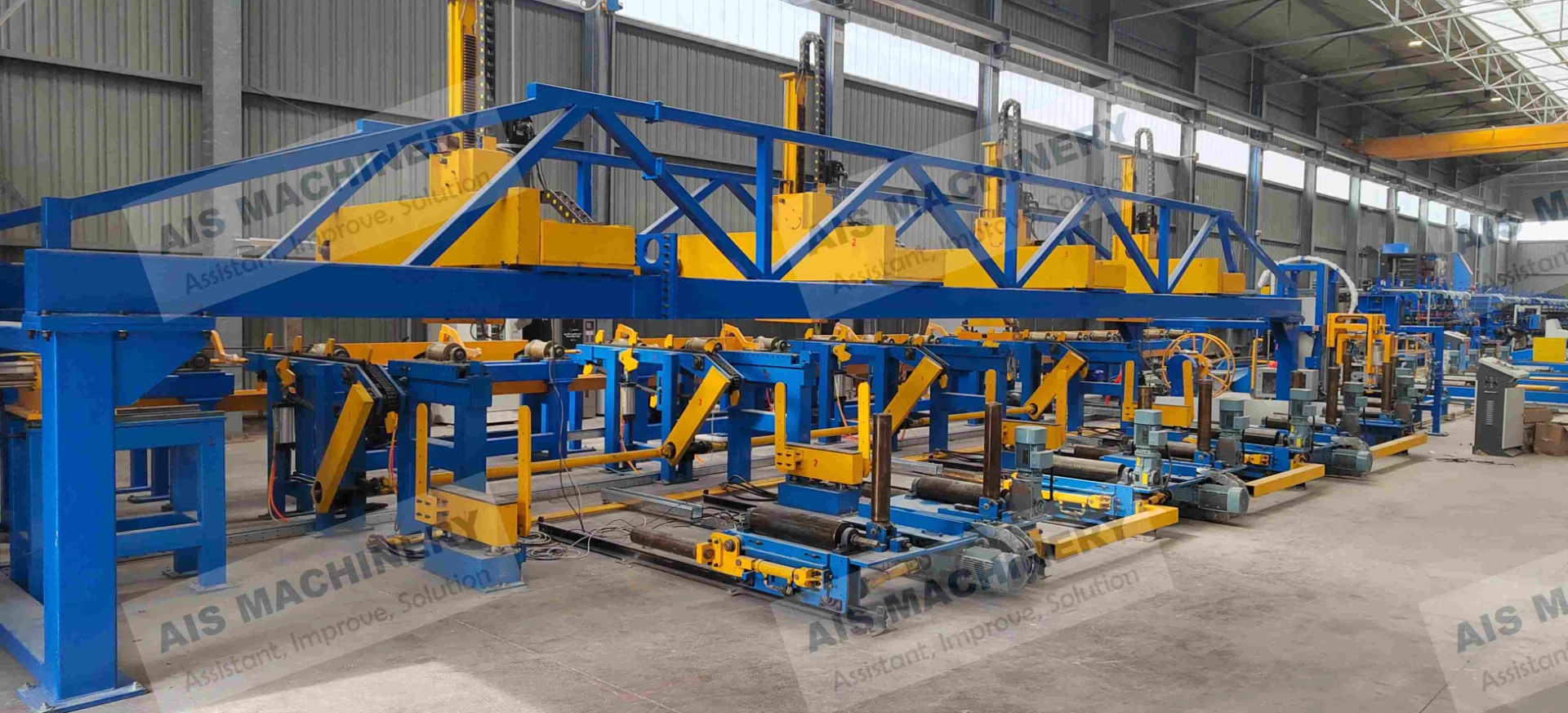
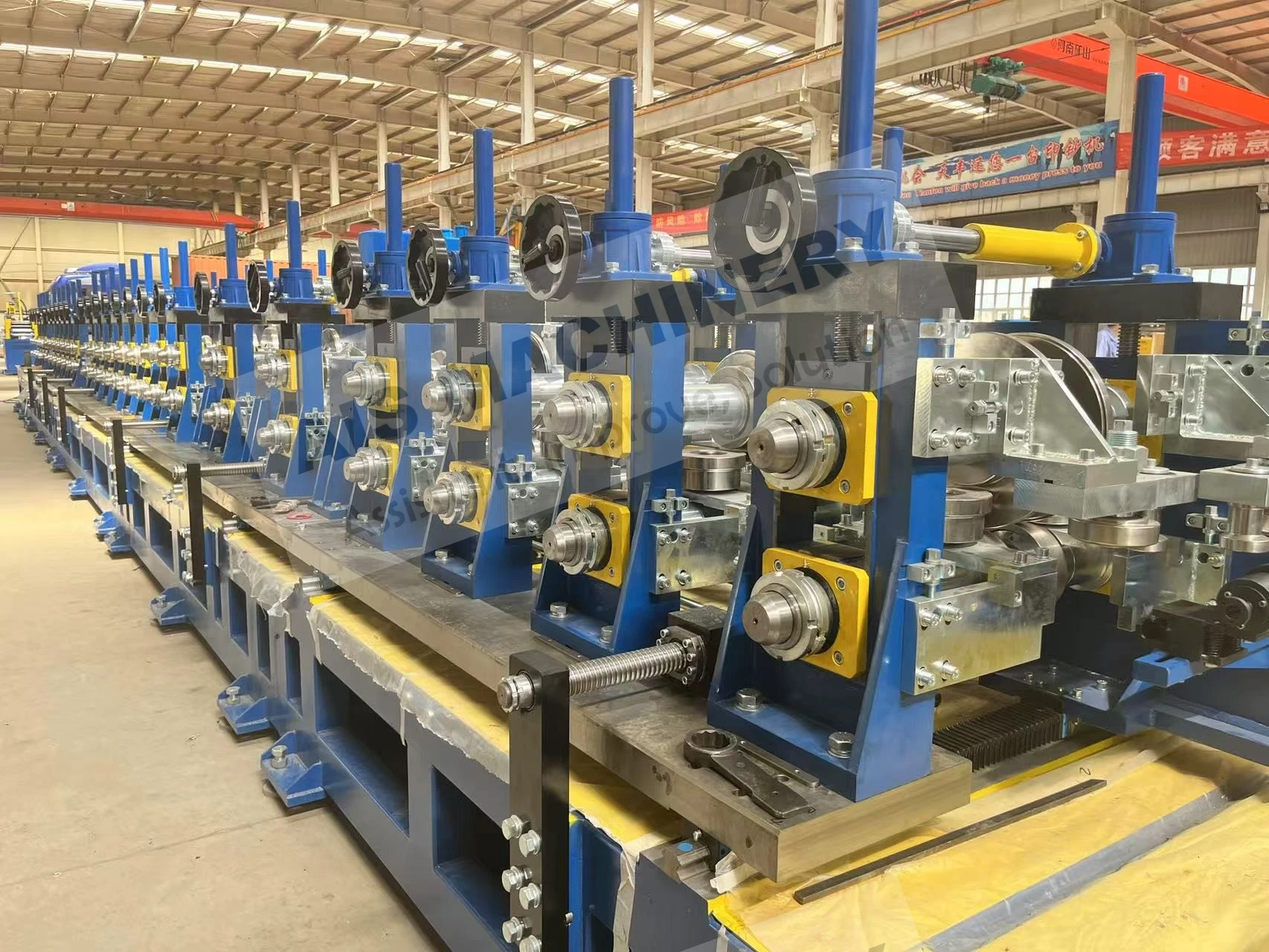
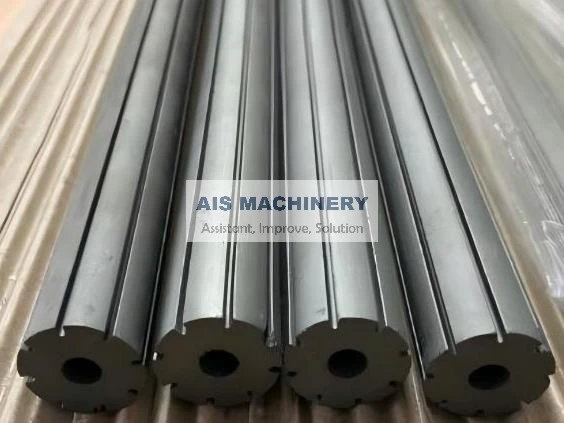
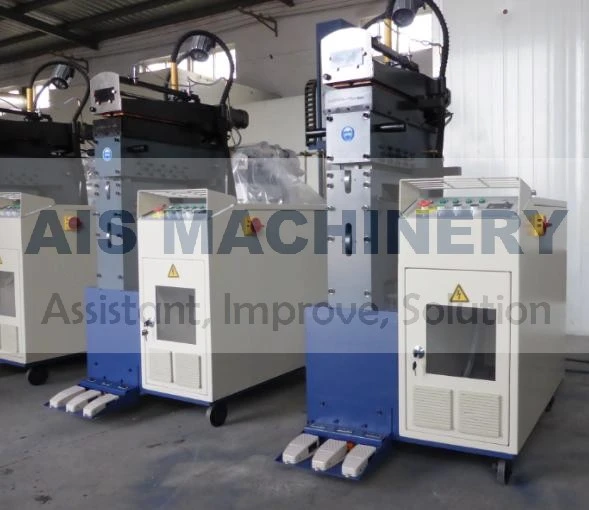
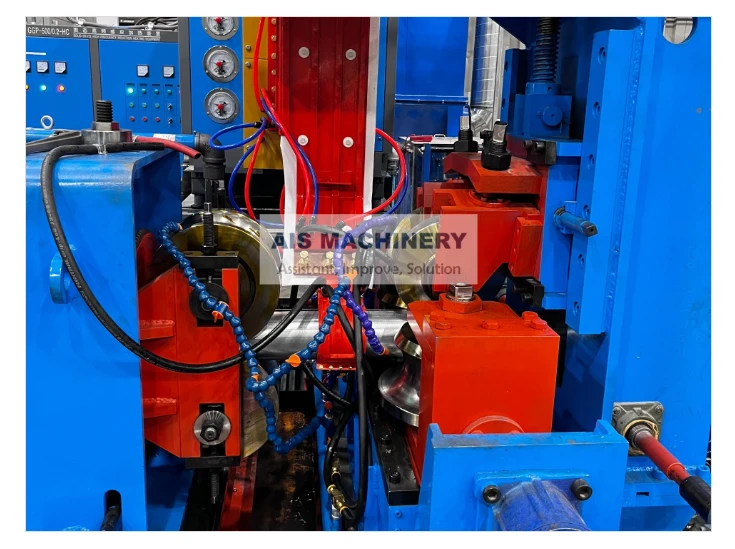
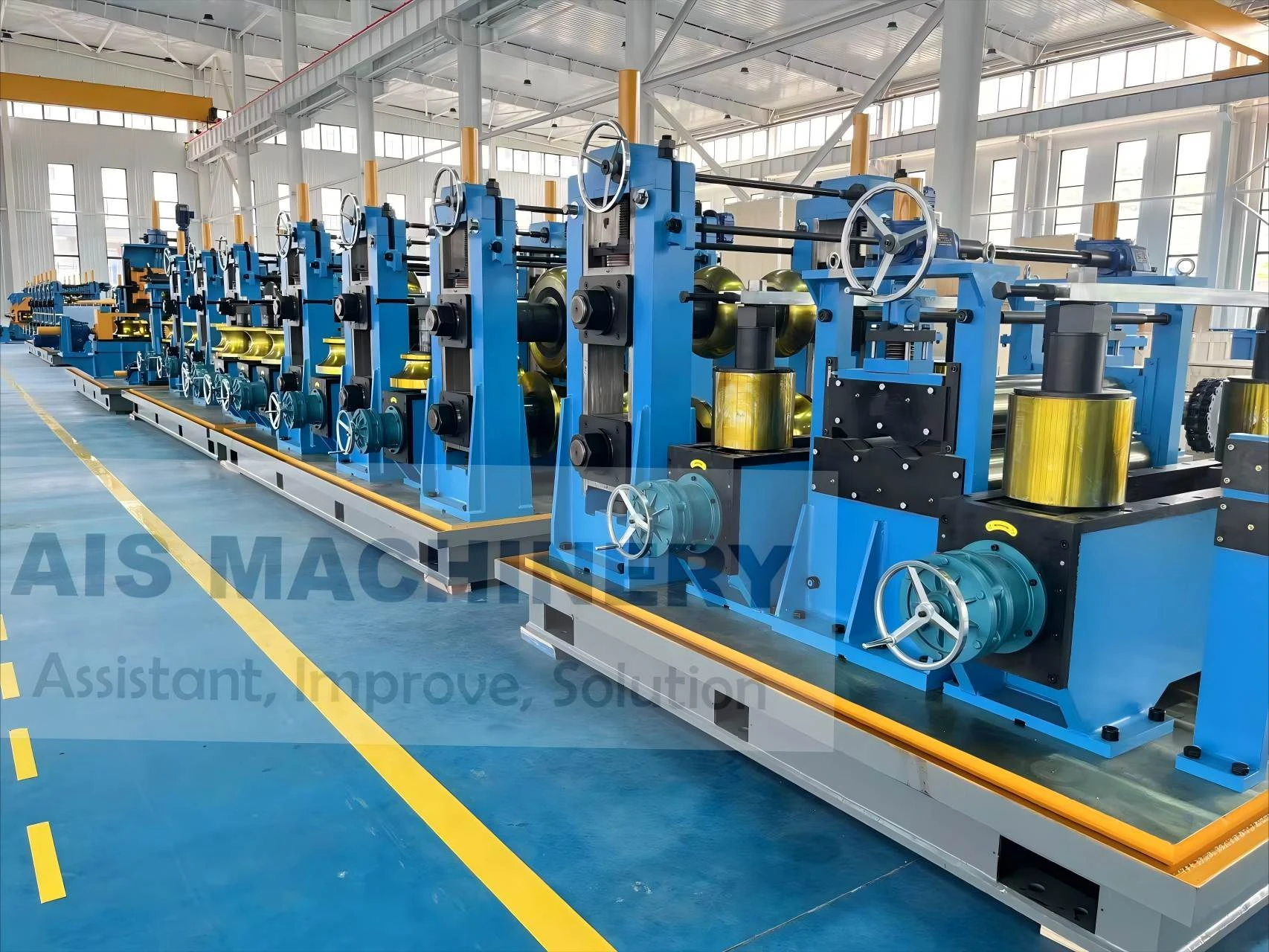
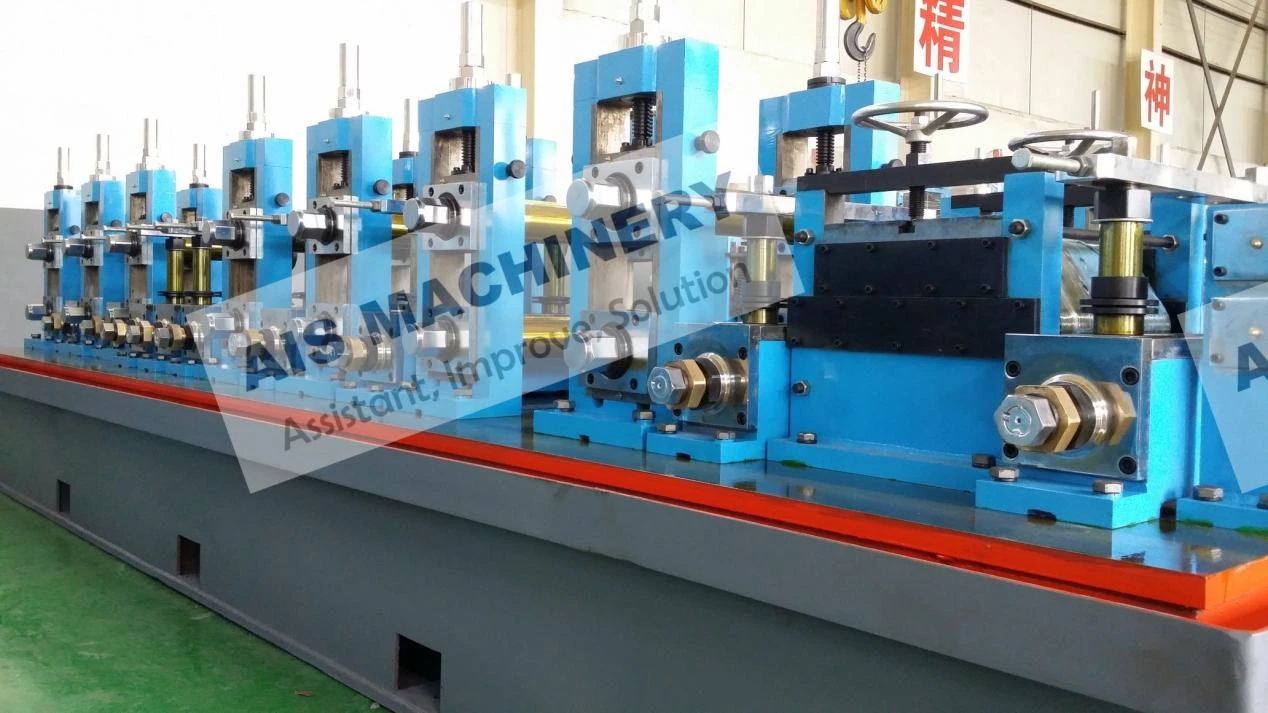
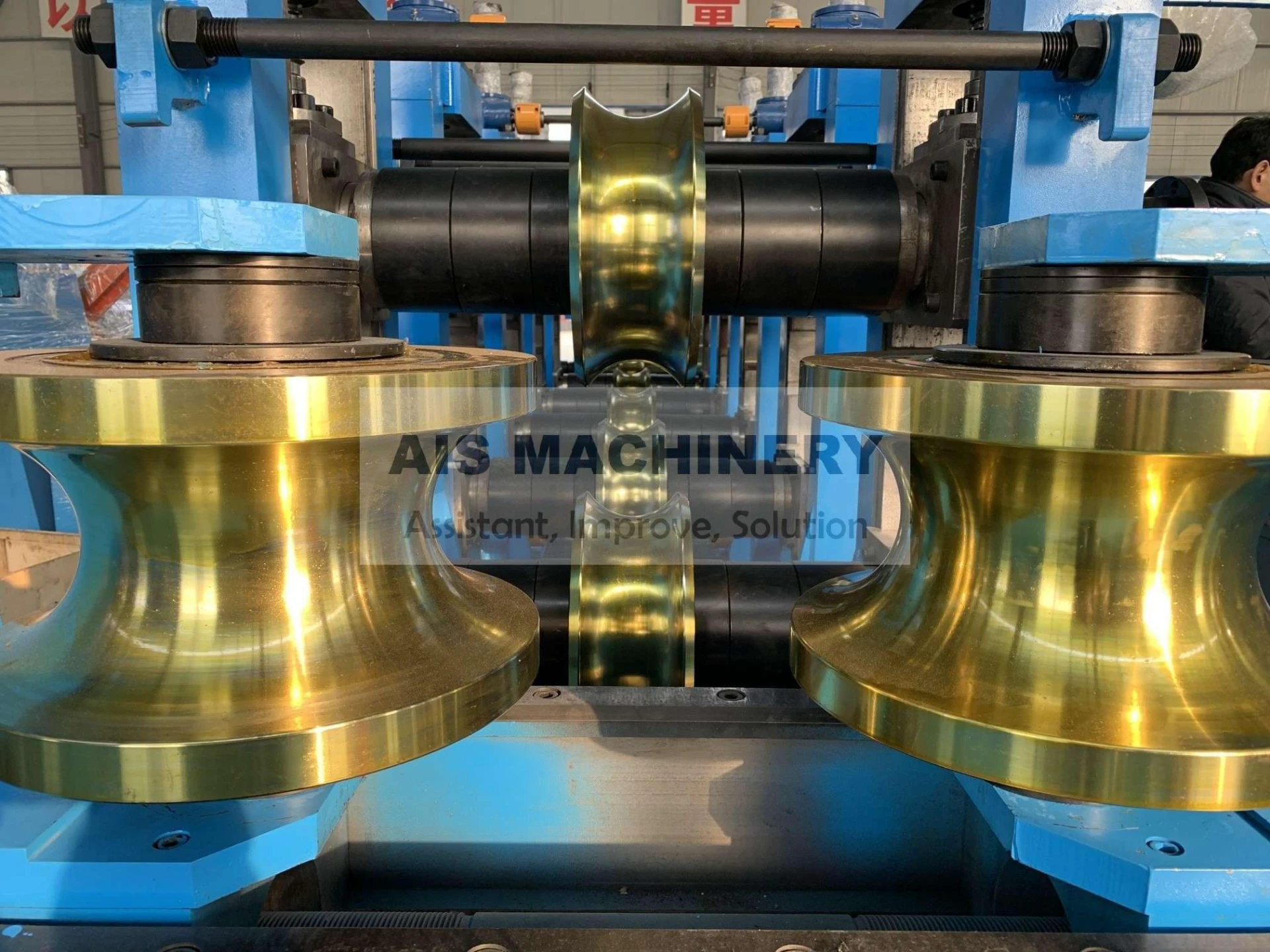
Cold roll forming is an advanced metalworking process that offers a multitude of benefits for manufacturing precision components. This technology has surged in popularity across various industries due to its efficiency, versatility, and ability to produce high-strength profiles. Having spent years researching and applying cold roll forming techniques, I've witnessed its transformative influence on modern production methodologies.
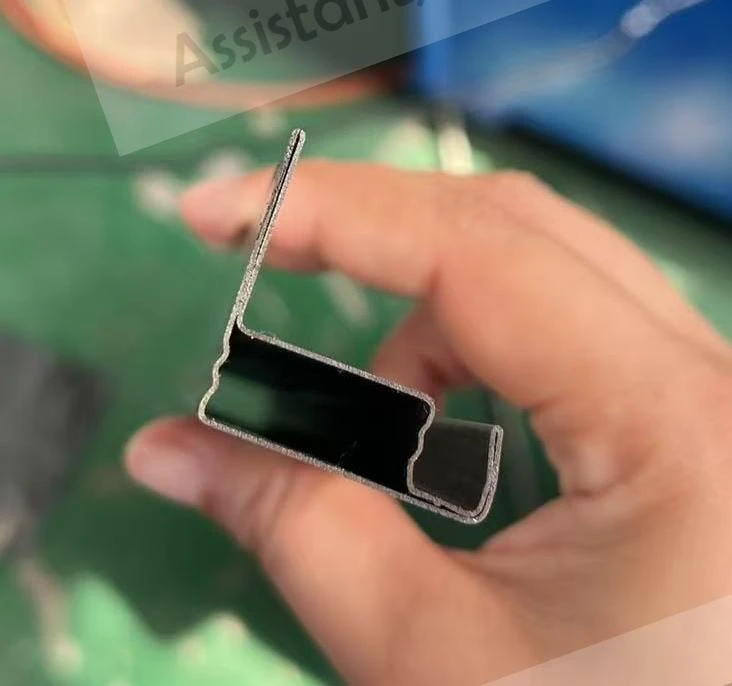
Moreover, the environmental advantages of cold roll forming should not be overlooked. Operating at room temperature means that this technique consumes less energy compared to heat-based forming processes. Additionally, the process generates less scrap, contributing to a more sustainable production cycle. As industries strive for greener manufacturing practices, cold roll forming stands out as an appealing option for reducing the carbon footprint of production. Through firsthand experience, it is evident that the adaptability of cold roll forming is unmatched. It accommodates a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, and copper, allowing manufacturers to tailor the material properties to specific application needs. The ability to integrate additional features, such as holes, notches, or embosses during the forming process, further enhances the versatility of cold roll forming. In conclusion, cold roll forming is an essential process in the toolkit of modern manufacturing. Its precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred method for producing high-quality, durable components across diverse industries. By leveraging this advanced technique, businesses can not only meet but exceed the expectations of contemporary engineering challenges. From aerospace components to innovative construction materials, cold roll forming delivers on its promise of quality and versatility. For any organization considering adopting this technology, it's crucial to partner with experienced specialists who understand the nuances of the process. Proper design, tool crafting, and process optimization are vital to unlocking the full potential of cold roll forming. As I've learned through extensive application and study, mastering cold roll forming can significantly contribute to a competitive edge in the manufacturing landscape.
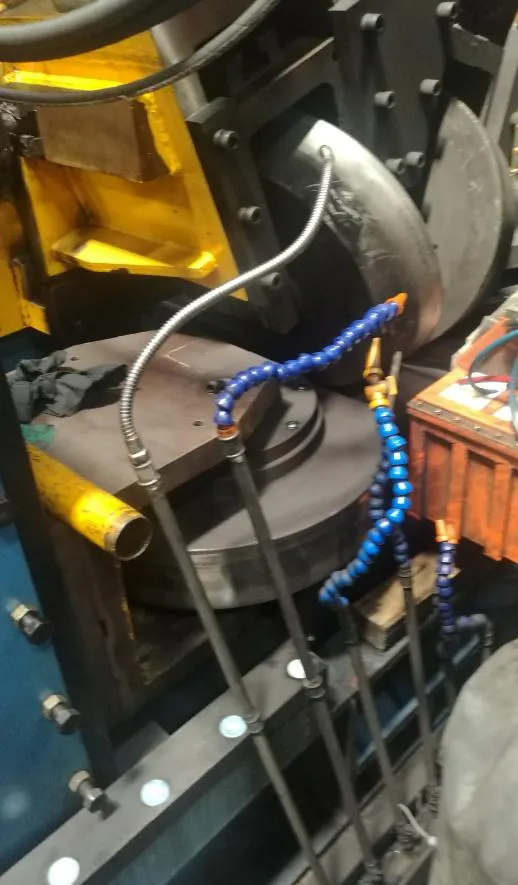
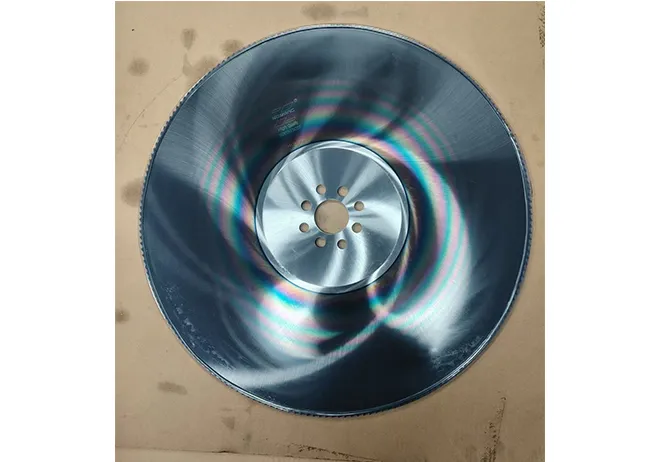


Moreover, the environmental advantages of cold roll forming should not be overlooked. Operating at room temperature means that this technique consumes less energy compared to heat-based forming processes. Additionally, the process generates less scrap, contributing to a more sustainable production cycle. As industries strive for greener manufacturing practices, cold roll forming stands out as an appealing option for reducing the carbon footprint of production. Through firsthand experience, it is evident that the adaptability of cold roll forming is unmatched. It accommodates a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, and copper, allowing manufacturers to tailor the material properties to specific application needs. The ability to integrate additional features, such as holes, notches, or embosses during the forming process, further enhances the versatility of cold roll forming. In conclusion, cold roll forming is an essential process in the toolkit of modern manufacturing. Its precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred method for producing high-quality, durable components across diverse industries. By leveraging this advanced technique, businesses can not only meet but exceed the expectations of contemporary engineering challenges. From aerospace components to innovative construction materials, cold roll forming delivers on its promise of quality and versatility. For any organization considering adopting this technology, it's crucial to partner with experienced specialists who understand the nuances of the process. Proper design, tool crafting, and process optimization are vital to unlocking the full potential of cold roll forming. As I've learned through extensive application and study, mastering cold roll forming can significantly contribute to a competitive edge in the manufacturing landscape.
Related Products
Related News
Send a Message
Dear customer, thank you for your attention! We provide high-quality machinery and equipment and look forward to your orders. Please inform us of your needs and we will respond quickly!