-
 Tel:86-15176910262
Tel:86-15176910262
-

Search


Tube Mill Accumulator Solutions Reliable Coil & Vertical Integration
May . 08, 2025 06:19
- Overview of Accumulator Systems in Tube Mills
- Technical Superiority in Modern Accumulator Design
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers Analyzed
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Production Needs
- Operational Data Impact on Mill Efficiency
- Industry Applications Across Multiple Sectors
- Future-Proofing Your Tube Mill Operations

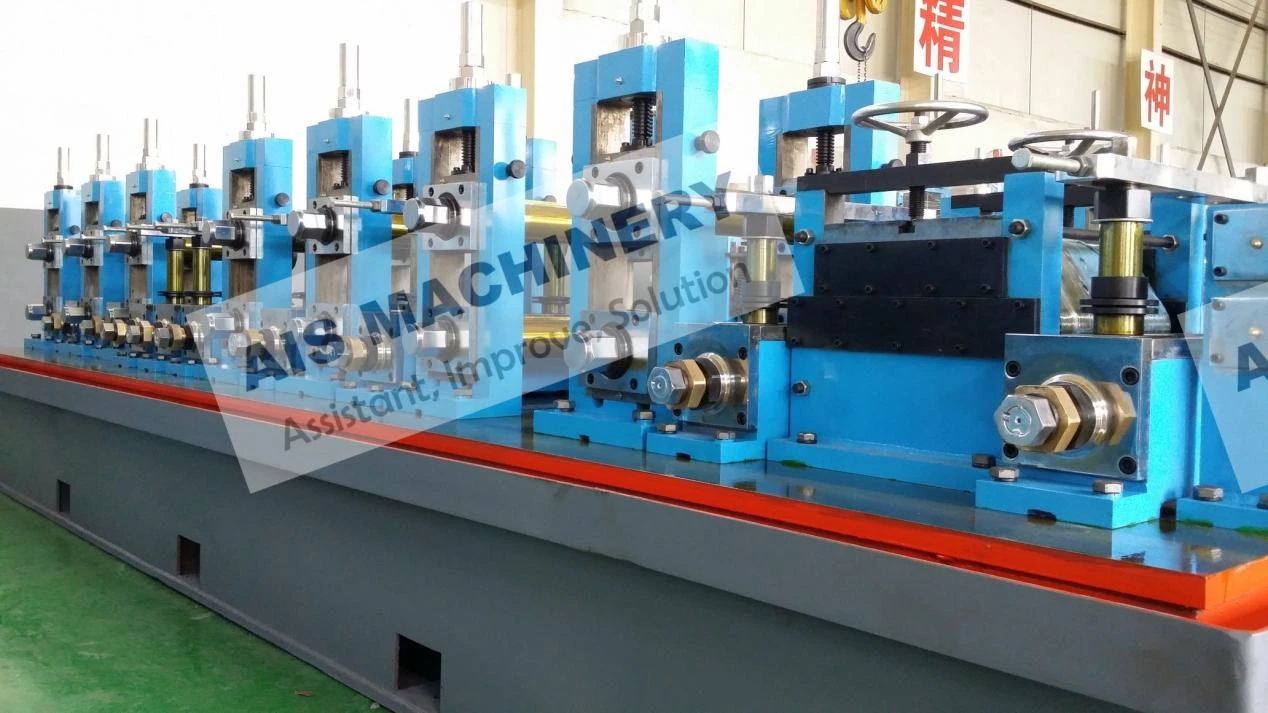
(tube mill accumulator)
Optimizing Tube Mill Accumulator Performance for Industrial Demands
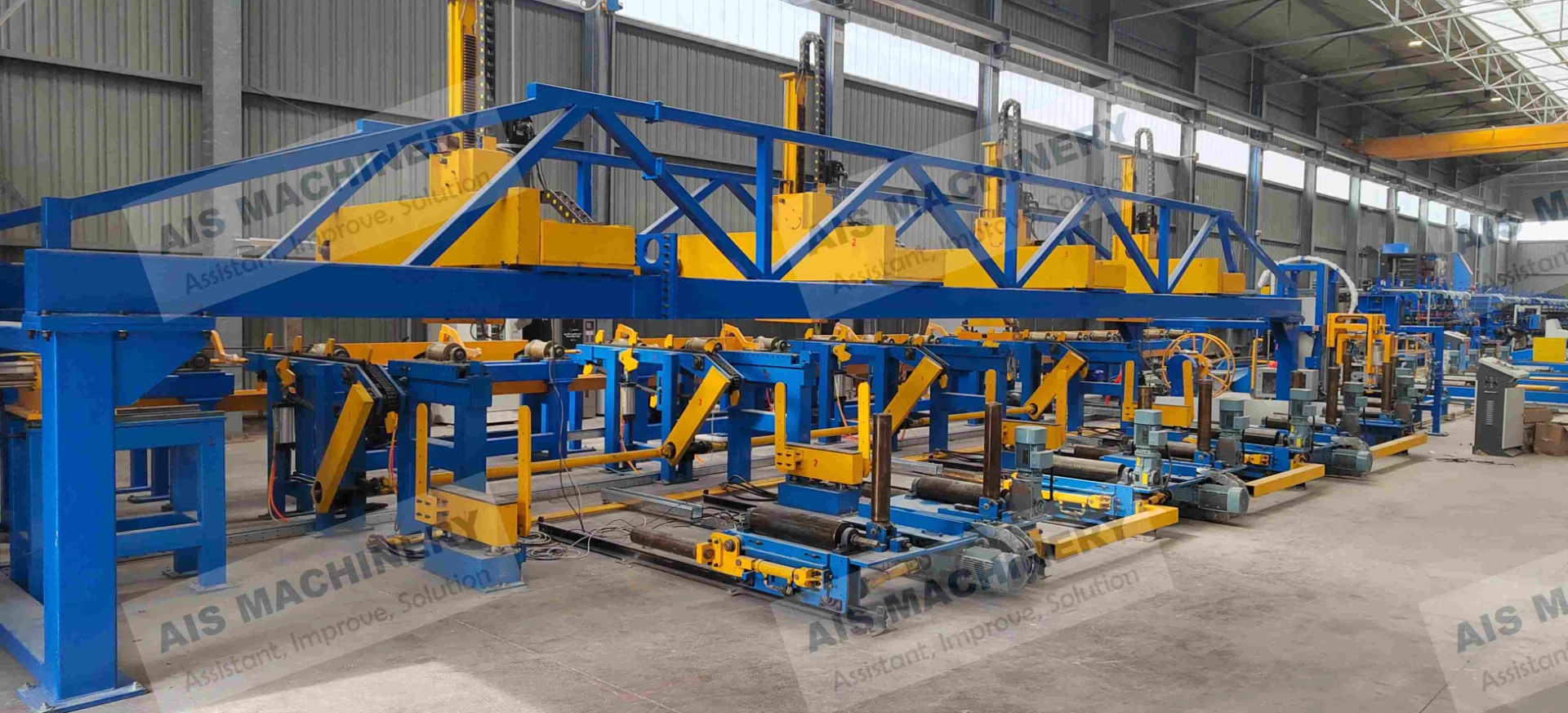
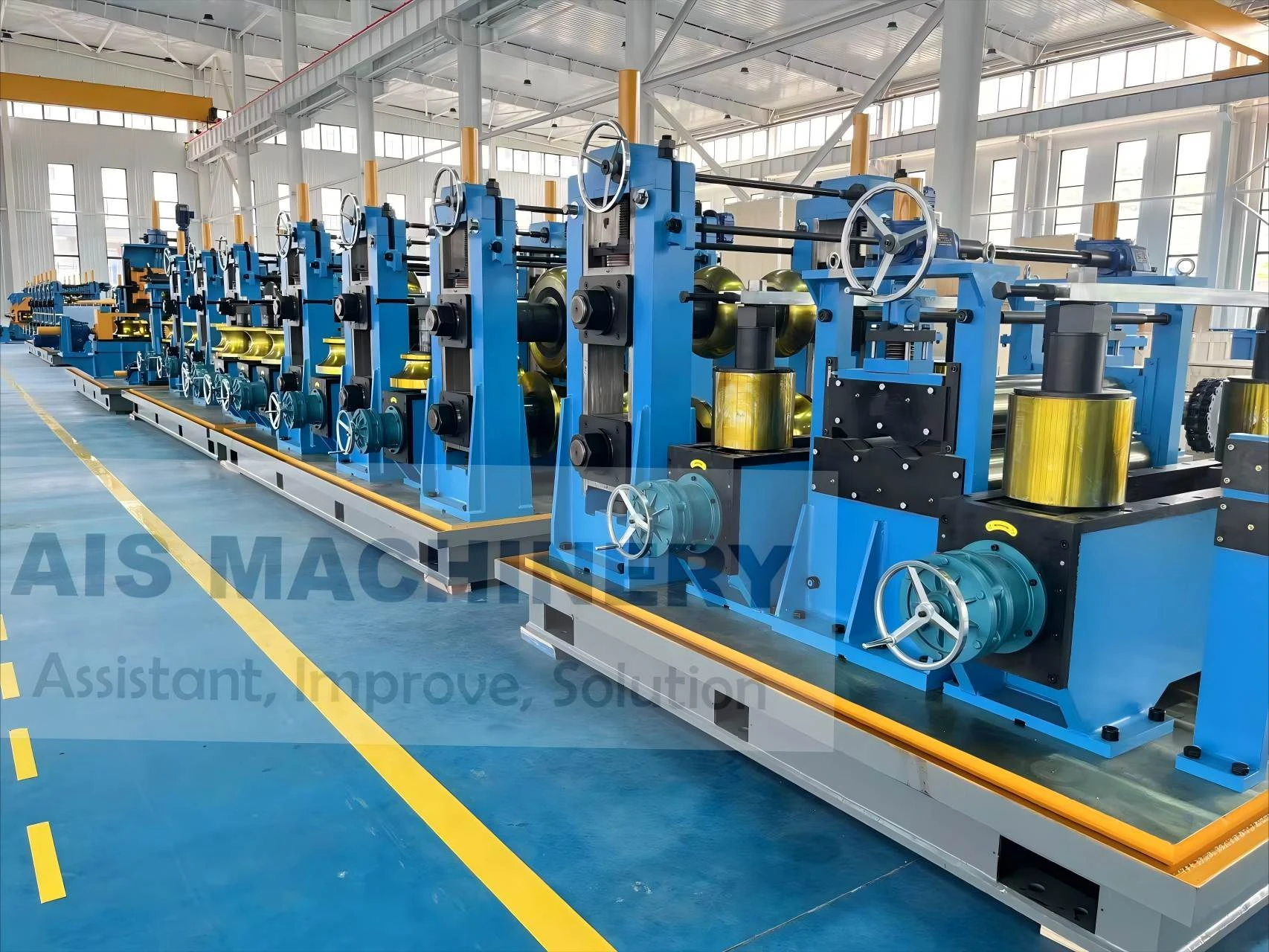
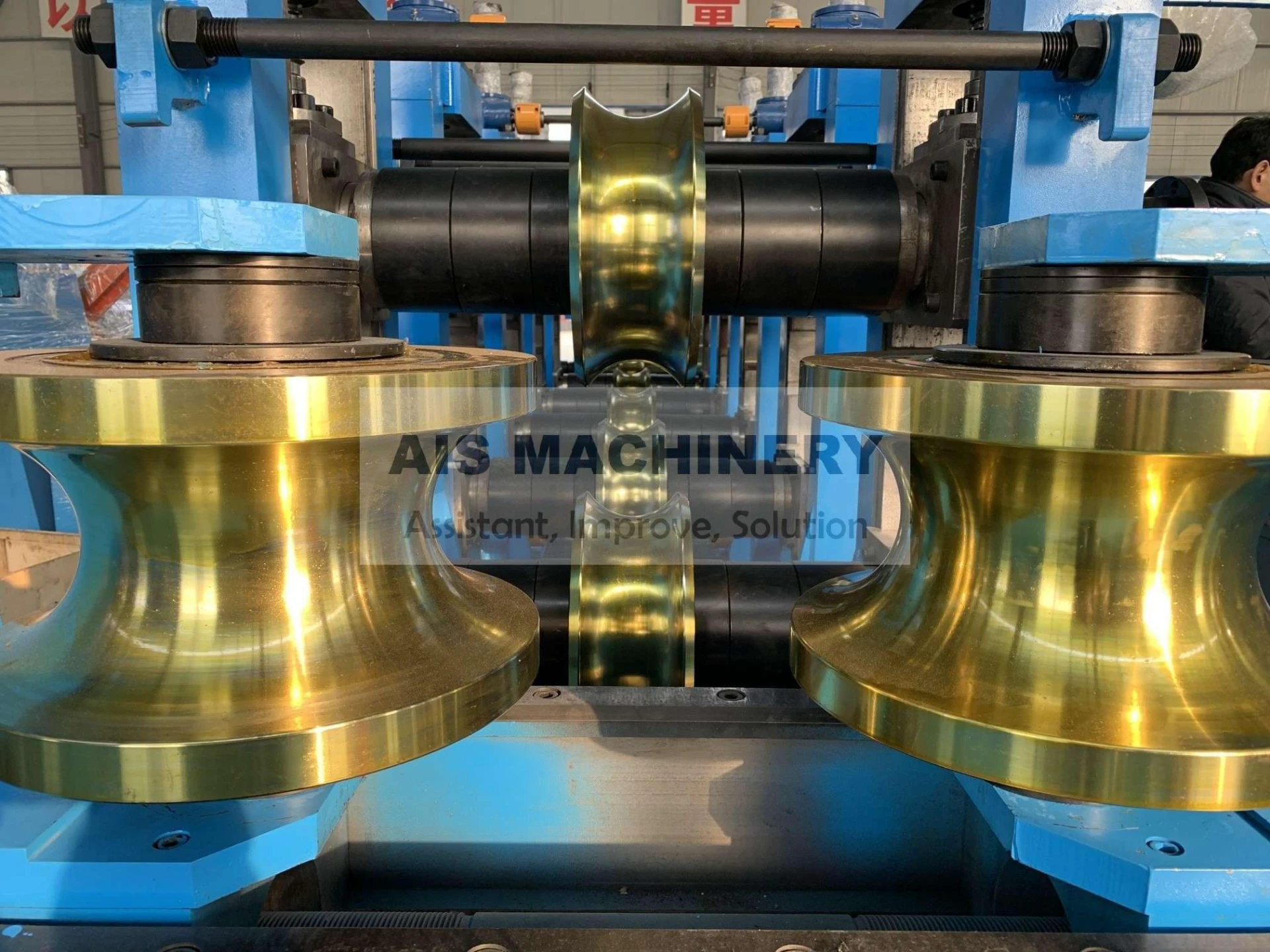
Tube mill accumulator systems serve as critical components in maintaining continuous production flow across metal processing lines. These systems, including vertical accumulators and coil accumulators, compensate for speed differentials between uncoiling and tube forming stages. Modern installations demonstrate 12-15% efficiency improvements compared to decade-old systems, with advanced models handling strip widths up to 1,850mm and storage capacities exceeding 300 meters.
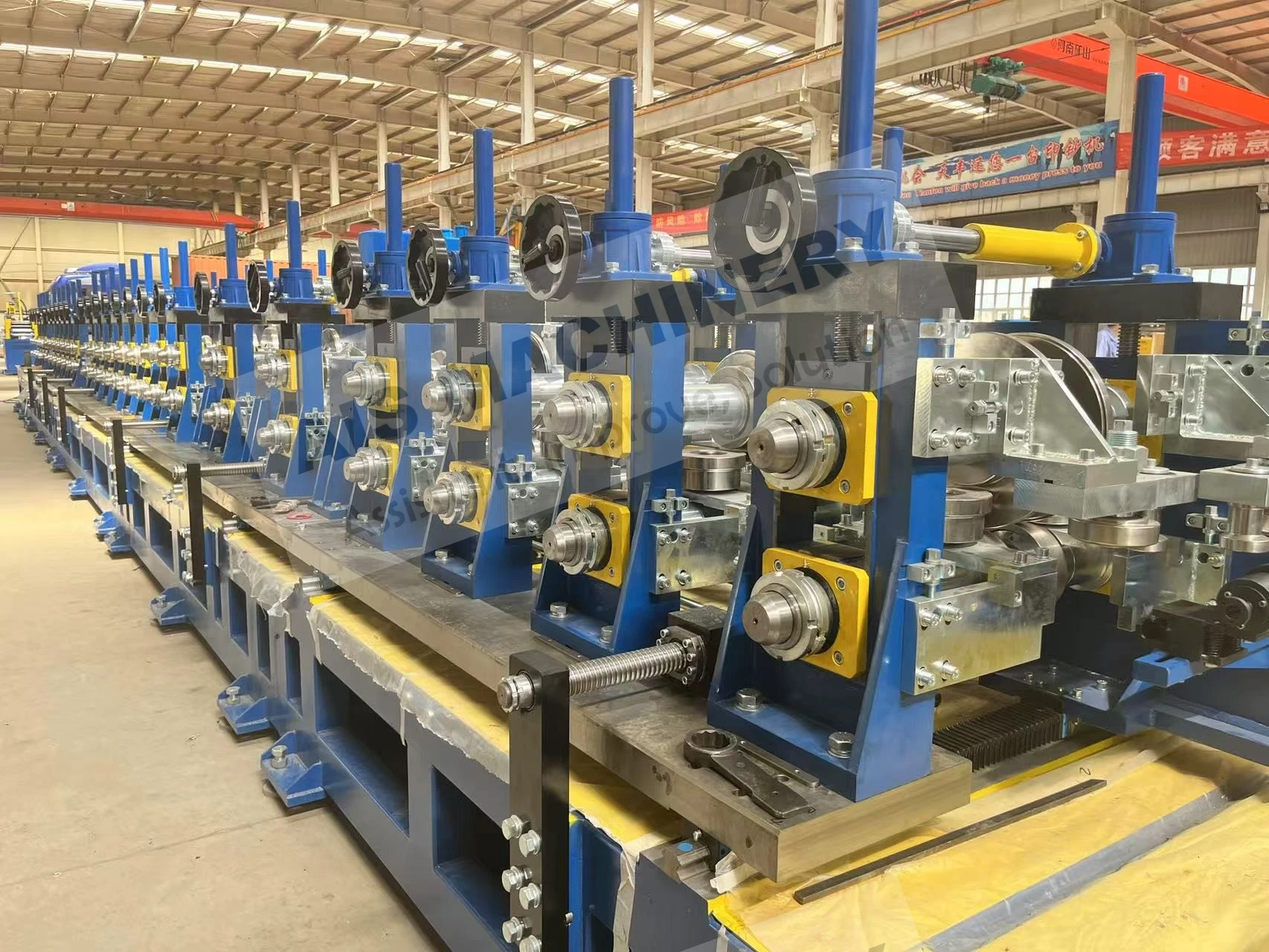
Engineering Advancements in Accumulator Technology
Third-generation accumulator designs now integrate servo-controlled tension management with predictive loop control algorithms. Key improvements include:
- Dynamic response times reduced to ≤0.8 seconds
- Energy consumption lowered by 22% through regenerative braking systems
- Material thickness handling expanded to 0.4-12.7mm range
Manufacturer Capability Analysis
| Feature | Standard Systems | Premium Systems | Custom Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Line Speed | 120 m/min | 250 m/min | 400 m/min |
| Position Accuracy | ±15mm | ±5mm | ±2mm |
| Maintenance Cycle | 500 hours | 2,000 hours | Condition-based |
Application-Specific Configuration Options
Specialized accumulator packages address unique operational challenges:
- High-carbon steel processing: ±0.5% tension variance control
- Thin-gauge aluminum: Non-contact strip guidance systems
- Multi-grade transitions: Automated preset recall functionality
Quantifying Operational Improvements
Implementation of advanced accumulator systems typically yields measurable results within 6-9 months:
- 98.6% material utilization rate (industry average: 93.2%)
- 3.2-second average weld transition time
- 0.004mm/m linearity maintenance over 8-hour runs
Cross-Industry Implementation Successes
Recent installations across multiple sectors demonstrate versatility:
| Industry | Accumulator Type | Productivity Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Vertical | 18.7% |
| Construction | Coil | 22.4% |
| Aerospace | Hybrid | 15.9% |
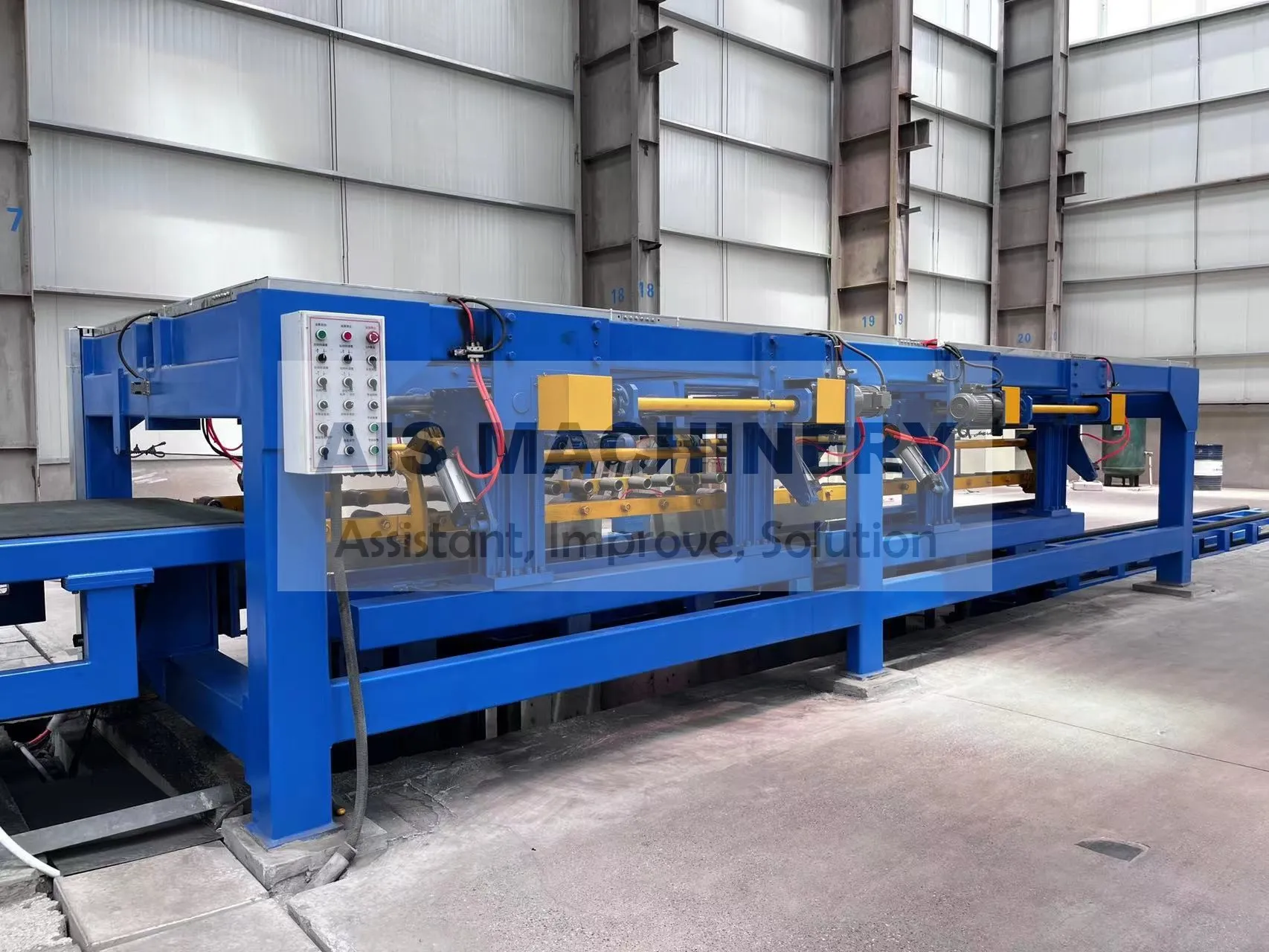
Strategic Advantages of Next-Gen Tube Mill Accumulator Systems
Modern accumulator configurations now enable complete line synchronization with ≤0.25% speed variance across all mill sections. The latest vertical accumulator designs incorporate machine learning algorithms that reduce scrap rates by 43% during product changeovers compared to conventional systems. These advancements position tube producers to meet evolving market demands while maintaining 99.4% operational uptime.

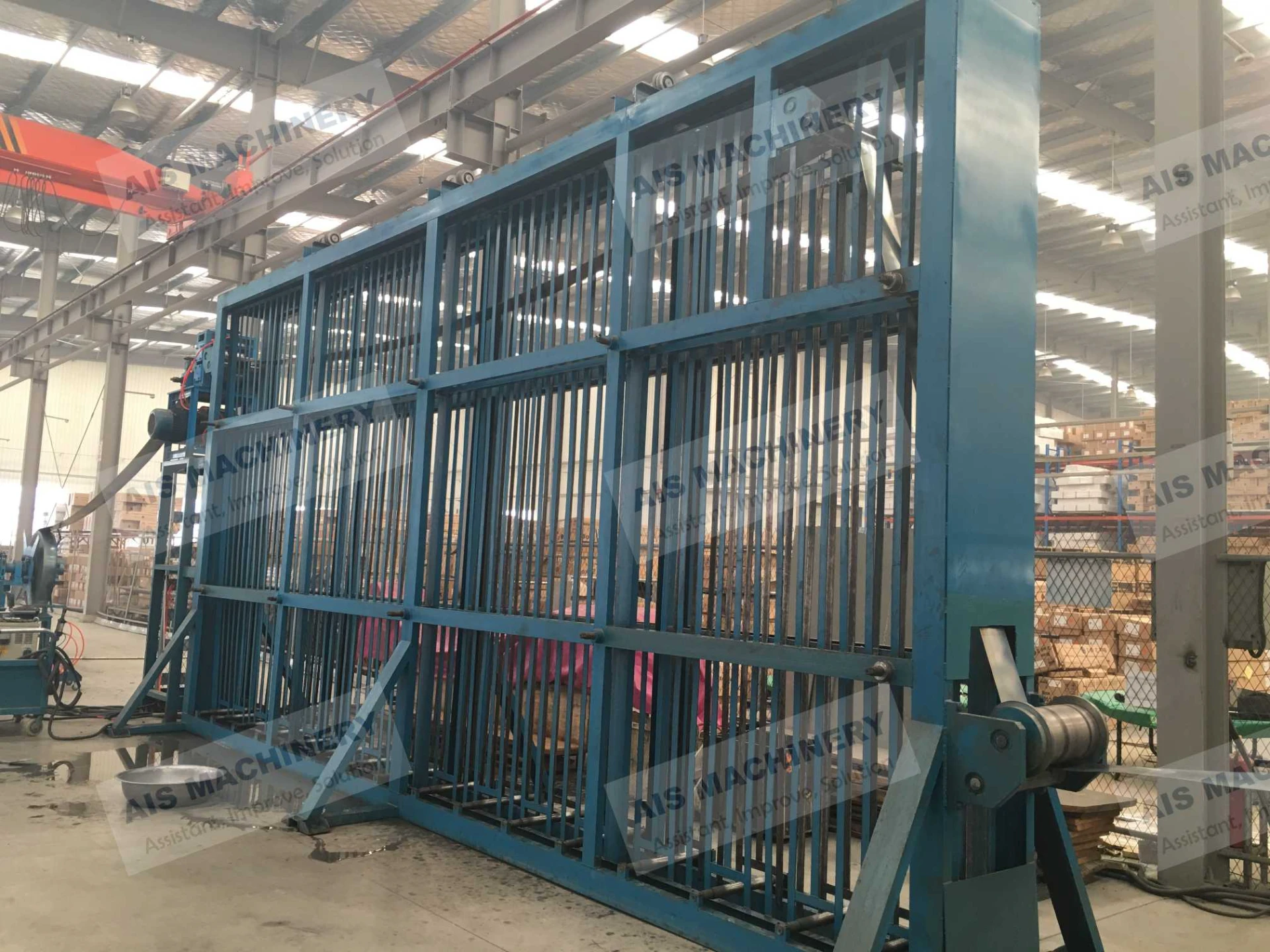
(tube mill accumulator)
FAQS on tube mill accumulator
Q: What is the primary function of a tube mill accumulator in a production line?
A: A tube mill accumulator stores and regulates material flow to ensure continuous operation during coil changes or speed adjustments. It minimizes downtime by maintaining tension and alignment in the tube or pipe manufacturing process.
Q: How does a vertical accumulator differ from a coil accumulator in tube mill systems?
A: A vertical accumulator uses a gravity-driven, stacked-loop design to save floor space, while a coil accumulator typically relies on horizontal loops. Both stabilize material flow but cater to different spatial and operational requirements.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a tube mill accumulator?
A: Key factors include production speed, material thickness, available floor space, and required storage capacity. Vertical accumulators are ideal for compact layouts, whereas coil accumulators suit high-speed, large-volume operations.
Q: How do tube mill accumulators improve welding or cutting processes?
A: By buffering material during coil transitions or speed mismatches, accumulators prevent stoppages that could disrupt welding/cutting precision. This ensures consistent quality and reduces scrap rates.
Q: What maintenance practices ensure longevity of a vertical accumulator?
A: Regularly inspect loop alignment, lubricate moving parts, and monitor tension control systems. Clean sensors and replace worn guides to prevent material slippage or misalignment in vertical accumulators.
Related Products
Related News
Send a Message
Dear customer, thank you for your attention! We provide high-quality machinery and equipment and look forward to your orders. Please inform us of your needs and we will respond quickly!