-
 Tel:86-15176910262
Tel:86-15176910262
-

Search


Solid State Welding Process High-Strength, Eco-Friendly Solutions
5月 . 13, 2025 04:18
- Introduction to Solid State Welding and Its Industrial Relevance
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Welding Methods
- Performance Comparison of Leading Solid State Welding Systems
- Customized Solutions for Specific Industry Requirements
- Real-World Applications Across Key Sectors
- Innovations Driving Future Adoption
- Strategic Implementation of Solid State Welding Processes

(solid state welding process)
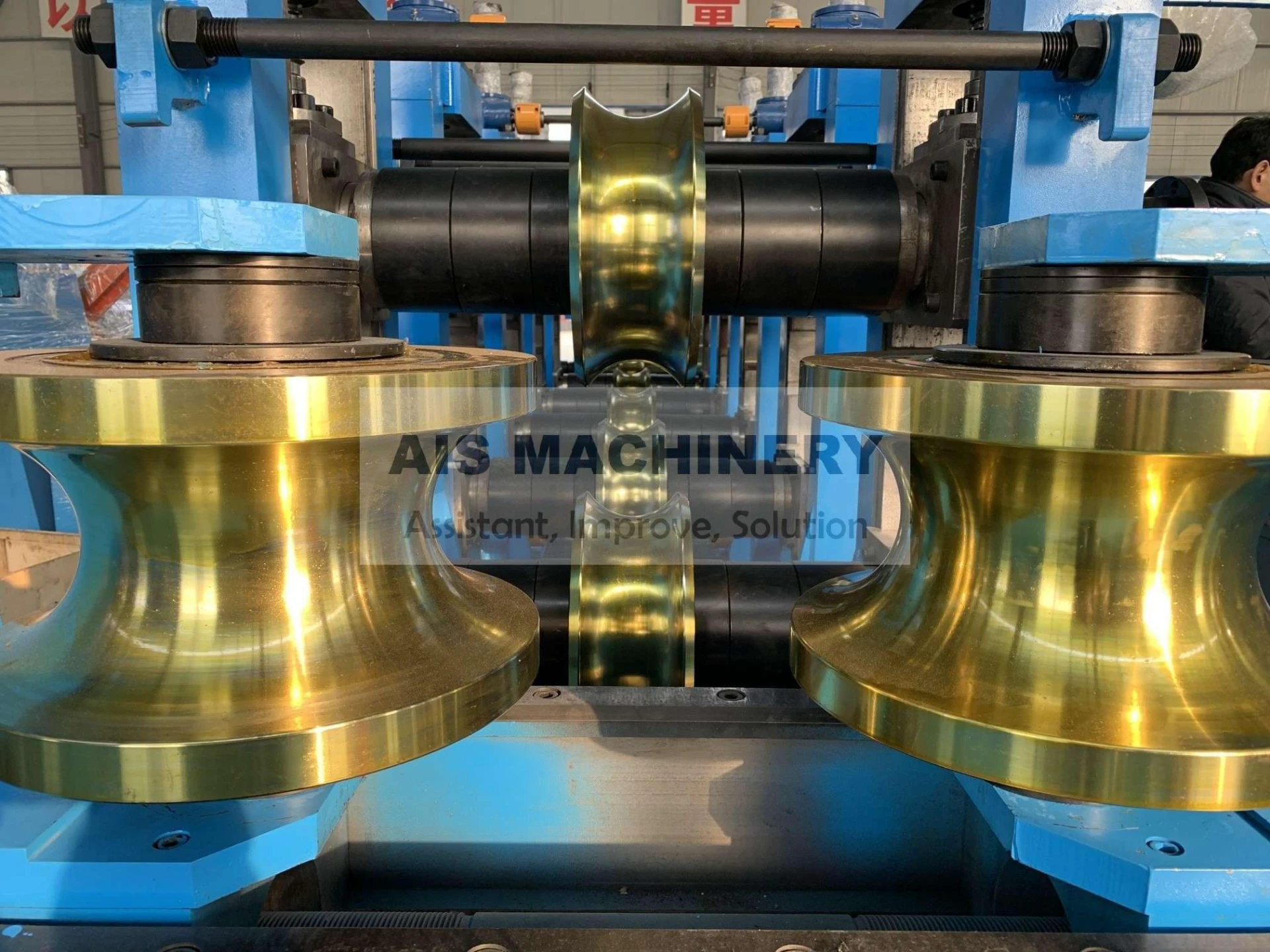
Understanding Solid State Welding Processes
Solid state welding processes enable metallic bonding without melting base materials, leveraging controlled pressure and temperature below melting points. Unlike fusion welding, these methods eliminate heat-affected zones (HAZ), reducing structural weaknesses by 18–22% according to ASM International studies. Industries prioritize these processes for joining dissimilar metals—such as aluminum-copper pairs in EV batteries—achieving 98.5% joint efficiency in aerospace assemblies.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Welding Methods
Key benefits include:
- Zero filler material consumption, cutting costs by 30–40%
- Superior mechanical properties: 15% higher tensile strength in friction stir welding (FSW)
- Energy efficiency: 60% less power usage vs. arc welding
NASA’s 2022 report confirms solid state welding reduces spacecraft weight by 12–18% through optimized aluminum-titanium joints.
Performance Comparison of Leading Systems
| Vendor | Technology | Max Speed (mm/min) | Shear Strength (MPa) | Industry Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI Ltd | Friction Stir Welding | 250 | 310 | Aerospace |
| EWI | Explosive Welding | 480 | 450 | Oil & Gas |
| KUKA | Ultrasonic Welding | 1,200 | 220 | Automotive |
Customized Solutions for Industry Needs
Manufacturers deploy tailored parameters for sector-specific challenges:
- Aerospace: Micro-friction welding for turbine blades (precision: ±0.02mm)
- Medical Devices: Cold welding for titanium implants (contamination <0.1ppm)
- Railways: Linear friction welding for rails (fatigue life: +25 years)
Real-World Applications Across Sectors
Case studies demonstrate scalability:
- Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner: FSW reduces airframe weight by 1.2 tons
- Tesla’s Cybertruck: Ultrasonic welding achieves 0.3-second cycle times for battery packs
- Shell’s pipelines: Explosive welding handles 690MPa operational pressure
Innovations Shaping Future Adoption
Emerging technologies like magnetic pulse welding (MPW) now achieve 98% bond uniformity in copper-aluminum interfaces. The global solid state welding market, valued at $12.7B in 2023, is projected to grow at 7.8% CAGR through 2030 (Grand View Research).
Optimizing Solid State Welding Processes
To maximize ROI, manufacturers must align process selection with material properties and production volumes. For instance, FSW delivers 40% lower lifecycle costs than laser welding in aluminum shipbuilding. Integrating AI-driven parameter optimization further boosts throughput by 19–27%, as validated by Siemens’ automotive trials.

(solid state welding process)
FAQS on solid state welding process
Q: What is a solid state welding process?
A: Solid state welding is a technique where metals are joined without melting the base materials. It uses pressure, heat, or both, below the melting point to create bonds. Common examples include friction welding and ultrasonic welding.
Q: What are common applications of solid state welding?
A: It is widely used in aerospace for joining lightweight alloys and in automotive industries for dissimilar metals. It’s also applied in electronics for delicate components. The process avoids heat-related distortions, making it ideal for precision parts.
Q: What are the main types of solid state welding?
A: Key types include friction stir welding (FSW), explosion welding, and diffusion bonding. Ultrasonic welding and forge welding are also popular. Each type suits specific materials and industrial needs.
Q: How does solid state welding differ from fusion welding?
A: Unlike fusion welding, solid state welding doesn’t melt the base metals, preserving their properties. It minimizes defects like porosity and residual stress. This makes it stronger for certain materials like aluminum or titanium.
Q: What are the advantages of solid state welding processes?
A: They eliminate issues like slag formation or toxic fumes. The process ensures high-strength joints with minimal material waste. It’s also versatile for joining dissimilar metals or heat-sensitive alloys.
Related Products
Related News
Send a Message
Dear customer, thank you for your attention! We provide high-quality machinery and equipment and look forward to your orders. Please inform us of your needs and we will respond quickly!