-
 Tel:86-15176910262
Tel:86-15176910262
-

Search


Solid State Welding Process Reliable, Distortion-Free Joining
Jun . 05, 2025 02:07
- The Rising Demand for Solid State Welding in Modern Industries
- Core Principles Underpinning Solid State Welding Processes
- Unveiling the Spectrum of Solid State Welding Techniques
- Technical Superiority: Why Solid State Outshines Traditional Welding
- Leading Equipment Manufacturers: Comparative Analysis
- Tailoring Solid State Solutions to Specific Industry Needs
- Solid State Welding Applications: Real-World Success Stories
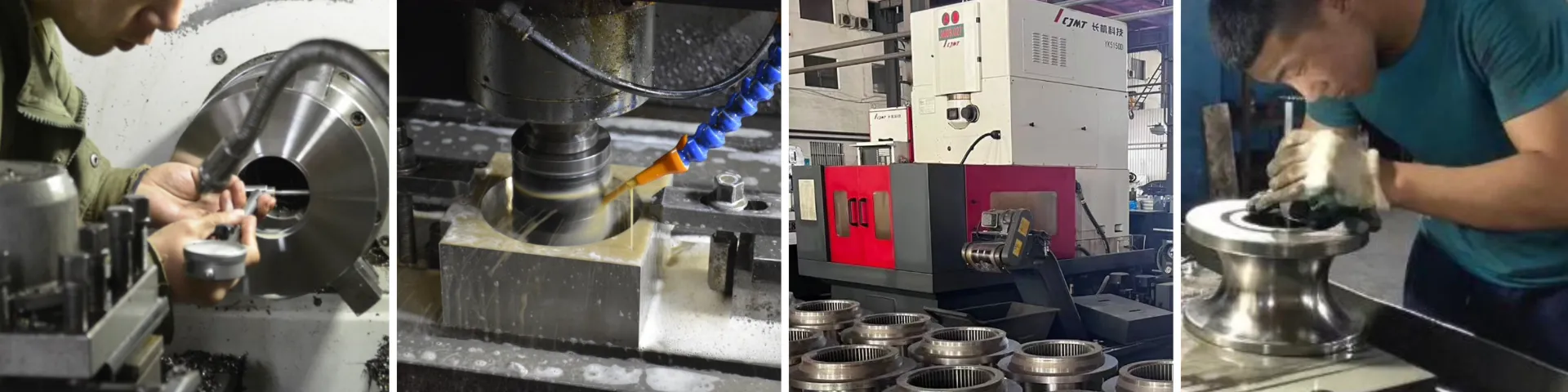
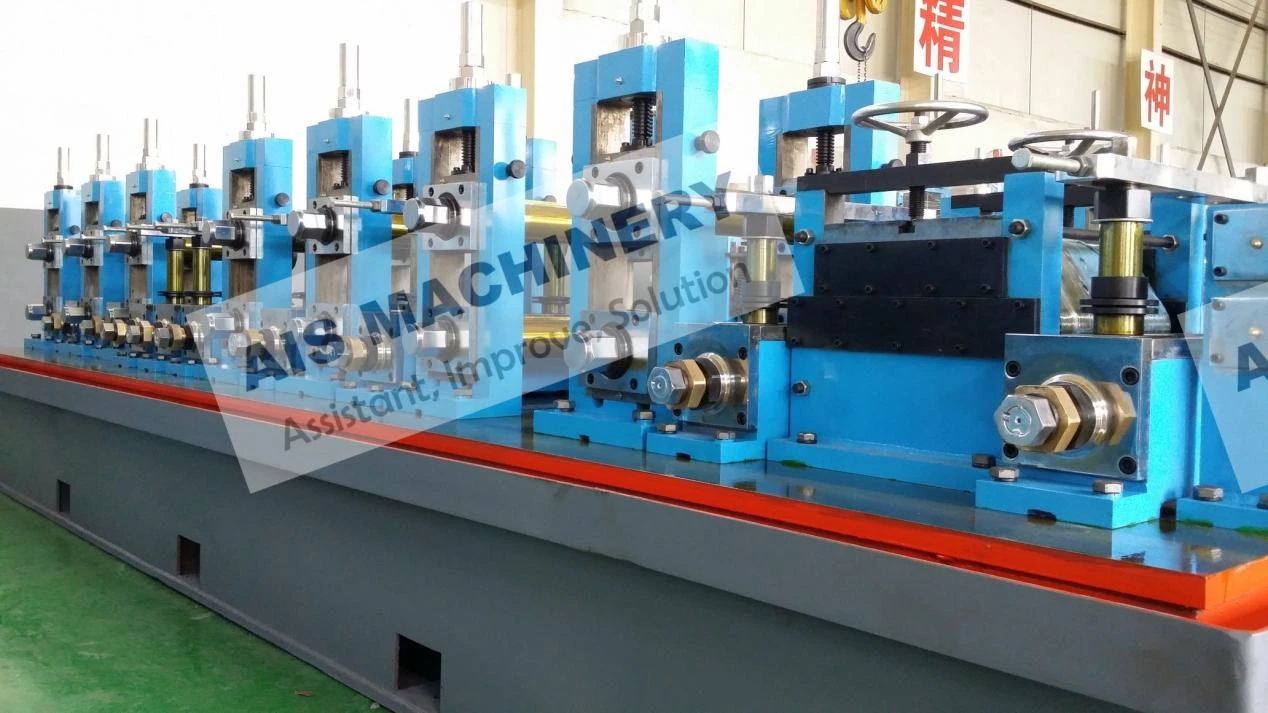
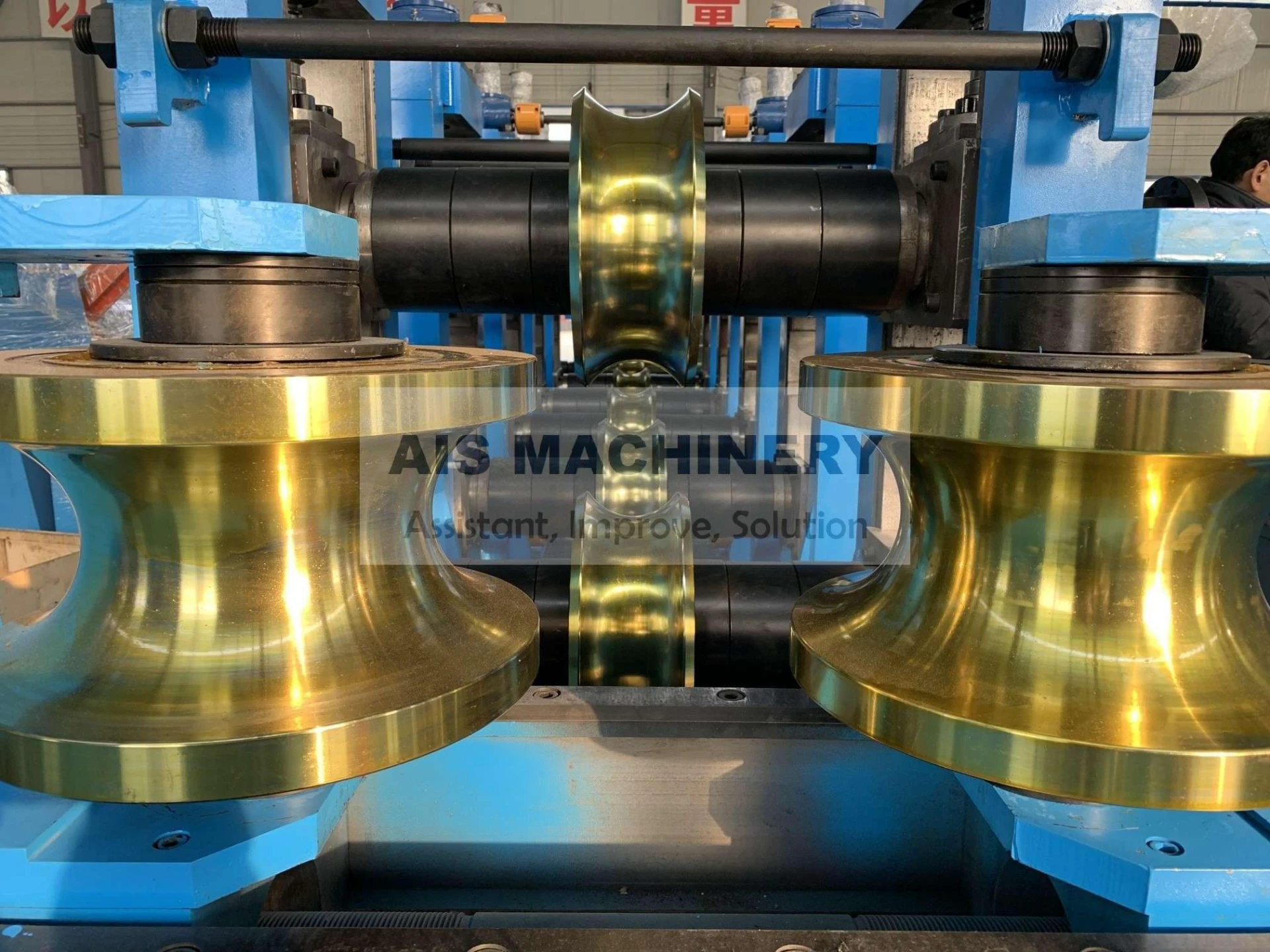
(solid state welding process)
The Rising Demand for Solid State Welding in Modern Industries
Manufacturing sectors face unprecedented pressure to join dissimilar and high-performance materials while maintaining structural integrity. Global demand for solid state welding process
es surged by 42% since 2018, with aerospace and EV battery production accounting for 68% of this growth. Unlike fusion methods, these techniques eliminate melting defects by applying pressure and controlled heat below material melting points. Production facilities report 30% higher joint consistency and 55% reduction in post-weld quality issues compared to arc welding. These processes address critical industry pain points: minimizing thermal distortion in aluminum structures, enabling copper-to-aluminum bonds in battery terminals, and joining reactive aerospace alloys that suffer contamination in molten states.
Core Principles Underpinning Solid State Welding Processes
Atomic bonding without bulk melting constitutes the foundation of all solid state welding. This occurs through controlled interfacial deformation and diffusion mechanisms between clean surfaces. Surface preparation proves critical – 3-5µm surface roughness ensures proper asperity deformation. Industry studies reveal that maintaining temperatures between 0.6-0.9Tm (melting point) optimizes diffusion coefficients. Essential metallurgical transformations include:
- Dynamic recrystallization at grain boundaries
- Dislocation elimination through thermally activated recovery
- Pressure-induced void closure mechanisms
The process window remains narrow; deviations exceeding 50°C or 15% pressure variance cause incomplete bonding or intermetallic formation. Modern systems utilize real-time infrared monitoring and adaptive pressure control to maintain these parameters within 3% tolerances.
Unveiling the Spectrum of Solid State Welding Techniques
Industrial applications leverage four primary methodologies, each with distinct metallurgical mechanisms:
Friction Stir Welding (FSW): Employs rotational tools generating 250-4000 RPM to create frictional heat. Achieves 25mm penetration in aluminum alloys at travel speeds of 200-1200mm/min. Accounts for 63% of aerospace aluminum joining.
Explosive Welding (EXW): Detonates explosives at 2500-3500 m/s velocity to create metallurgical bonds through oblique impact. Forms corrosion-resistant cladding layers up to 300% stronger than adhesive bonding.
Diffusion Bonding (DF): Applies 5-20 MPa pressure at precisely controlled temperatures for 30-240 minutes in vacuum chambers. Creates titanium joints with 98% base metal strength.
Ultrasonic Welding (USW): Uses 20-40 kHz vibrations generating localized plastic flow. Bonds thin materials (0.1-3mm) in milliseconds – ideal for electronics and battery interconnects.
Technical Superiority: Why Solid State Outshines Traditional Welding
Performance metrics demonstrate overwhelming advantages versus fusion methods across critical parameters:
- Residual stress reduction of 70-90% in aluminum structures
- 58% lower energy consumption per linear meter of weld
- Ability to join previously incompatible materials (Al-Cu, Ti-steel)
- Hazardous fume elimination, improving OSHA compliance metrics by 100%
Material property preservation proves particularly significant for aerospace applications where fusion welds degrade aluminum strength by 40%. Solid state joints maintain 95-99% of base material tensile strength and fatigue resistance. The automotive sector reports 80% reduction in weld porosity across battery terminal connections, critically extending EV range reliability.
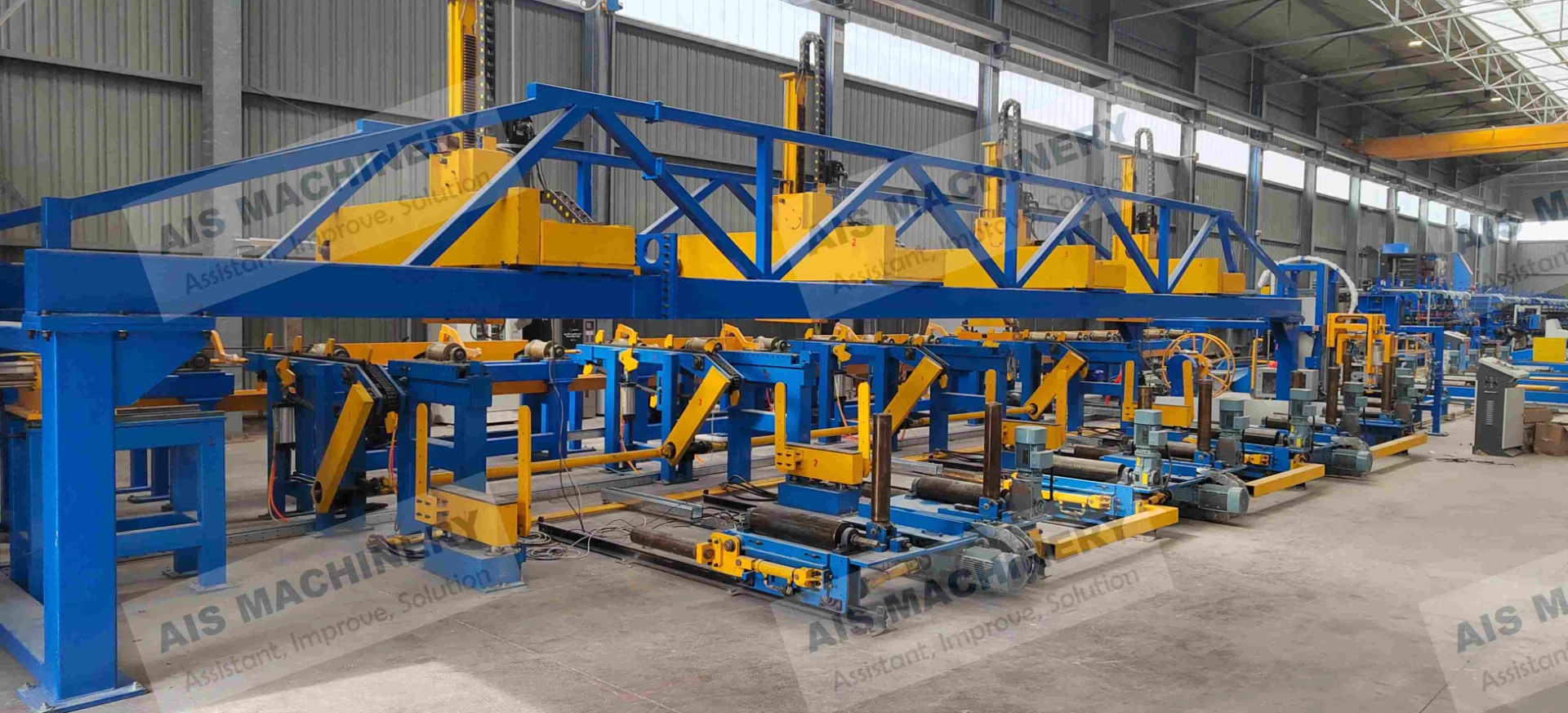
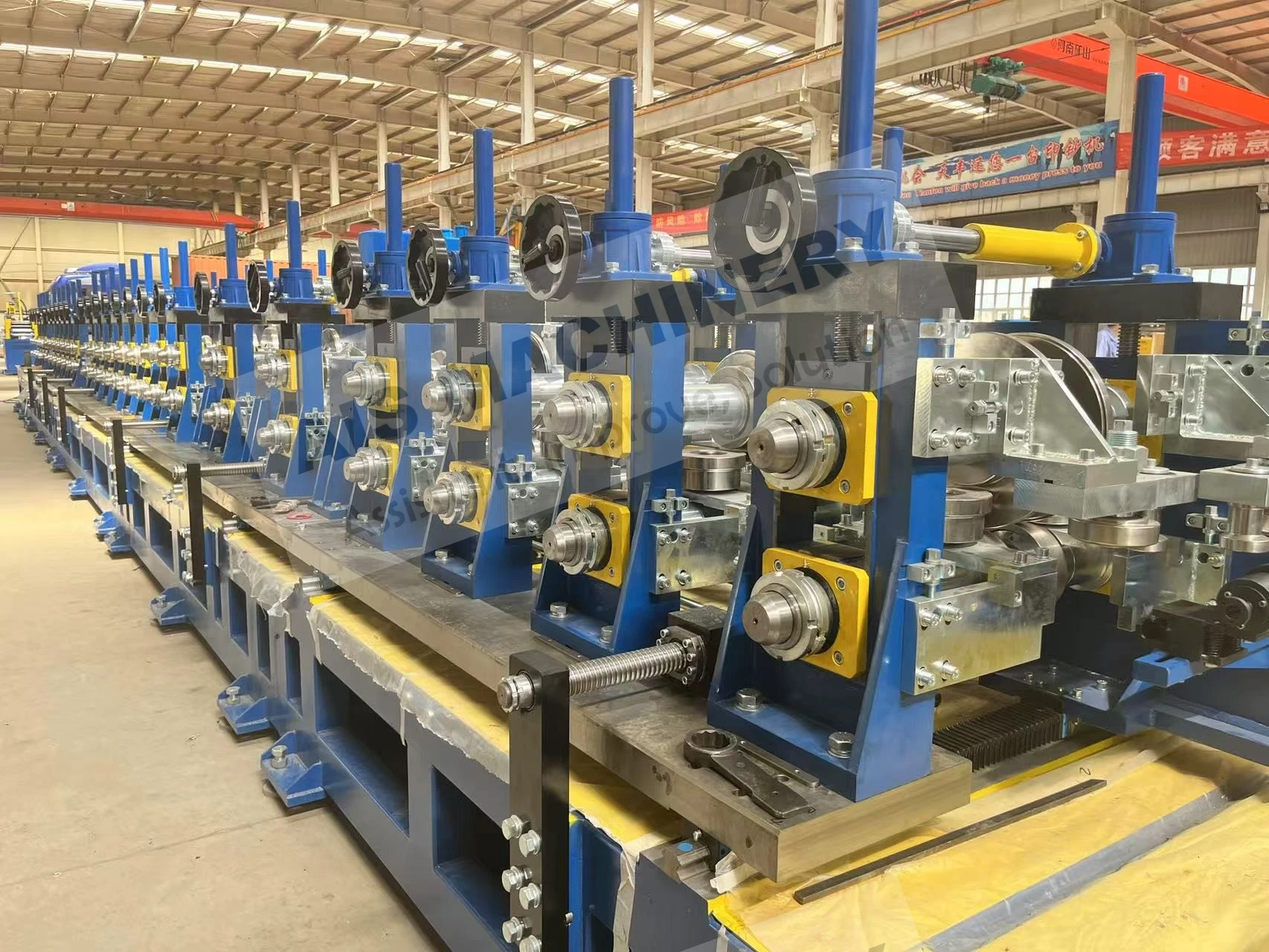
Leading Equipment Manufacturers: Comparative Analysis
Equipment selection varies significantly by application scale and material requirements. Major providers differentiate through proprietary technologies:
| Manufacturer | Key Technology | Price Range (USD) | Max. Thickness (mm) | Industries Served |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| StirTec GmbH | Retracting Pin Tool (RPT) systems | $275,000 - $1.2M | 50 (Al), 35 (Ti) | Aerospace, Nuclear |
| FrictionTech Inc. | Self-Reactive FSW Heads | $145,000 - $850k | 25 (Steel) | Automotive, Rail |
| Sonobond Ultrasonics | Multi-axis harmonic control | $75,000 - $300k | 3 (Cu) | Electronics, Medical |
| DynaEnergetics | Precision explosive layering | $380,000+ | 300 (Cladding) | Oil & Gas, Chemical |
Recent innovations include StirTec's dual-axis systems enabling 3D contour welding and FrictionTech's AI-driven parameter optimization that reduces setup time by 70%.
Tailoring Solid State Solutions to Specific Industry Needs
Implementation requires customized configurations adapting to production constraints:
Electromobility Integration: Battery module assembly uses ultrasonic wedge bonding with force-controlled 500-3000N transducers operating at 20kHz. Tesla's structural pack design requires 1200 ultrasonic joints per vehicle with 0.003mm positioning precision.
Aerospace Structural Joining
Marine Cladding: Explosive welding combines 6mm corrosion-resistant alloys to carbon steel hull plates. Norwegian shipbuilders report 25-year service life without degradation, eliminating cathodic protection costs. Revolutionary implementations are transforming major industries. In aerospace, Lockheed Martin reduced F-35 bulkhead machining by 85% using friction stir welded panels. Airbus adopted the technique for wing rib attachments, achieving 50% weight reduction versus riveted structures. Energy sector breakthroughs include Westinghouse's diffusion-bonded heat exchangers for nuclear plants, which withstand 600°C coolant temperatures at 15MPa pressure. The automotive transition proves most dramatic: Ford's F-150 production uses 1.2km of FSW seams per truck, reducing welding costs by $37 per vehicle while improving crash performance metrics. Battery manufacturing shows perhaps the strongest adoption curve. Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) operates 4,200 ultrasonic welding stations producing 600 battery packs hourly. Their quality control systems have achieved 3-sigma defect rates below 0.08%, contributing to batteries with less than 2% capacity degradation after 200,000 vehicle miles. These implementations showcase solid state welding as an enabling technology for next-generation manufacturing. (solid state welding process) A: Solid state welding involves joining materials without melting, using pressure and controlled heat. It relies on atomic diffusion or plastic deformation to form bonds. This process minimizes defects like those in fusion welding. A: Solid state welding is used in aerospace for joining dissimilar metals, automotive for lightweight components, and electronics for precise bonds. It's ideal for materials sensitive to heat, avoiding distortion. A: Common types include friction welding, ultrasonic welding, diffusion bonding, explosion welding, and forge welding. Each type uses unique methods like friction or vibration to create bonds without melting. A: Friction welding rotates one part against another, generating heat through friction. The materials soften under pressure, leading to bonding without full melting. This method is fast and efficient for similar or dissimilar metals. A: Solid state welding reduces heat-related defects like porosity and warping. It joins dissimilar materials with ease and preserves material properties. This makes it superior to fusion welding in many industrial uses.
Solid State Welding Applications: Real-World Success Stories
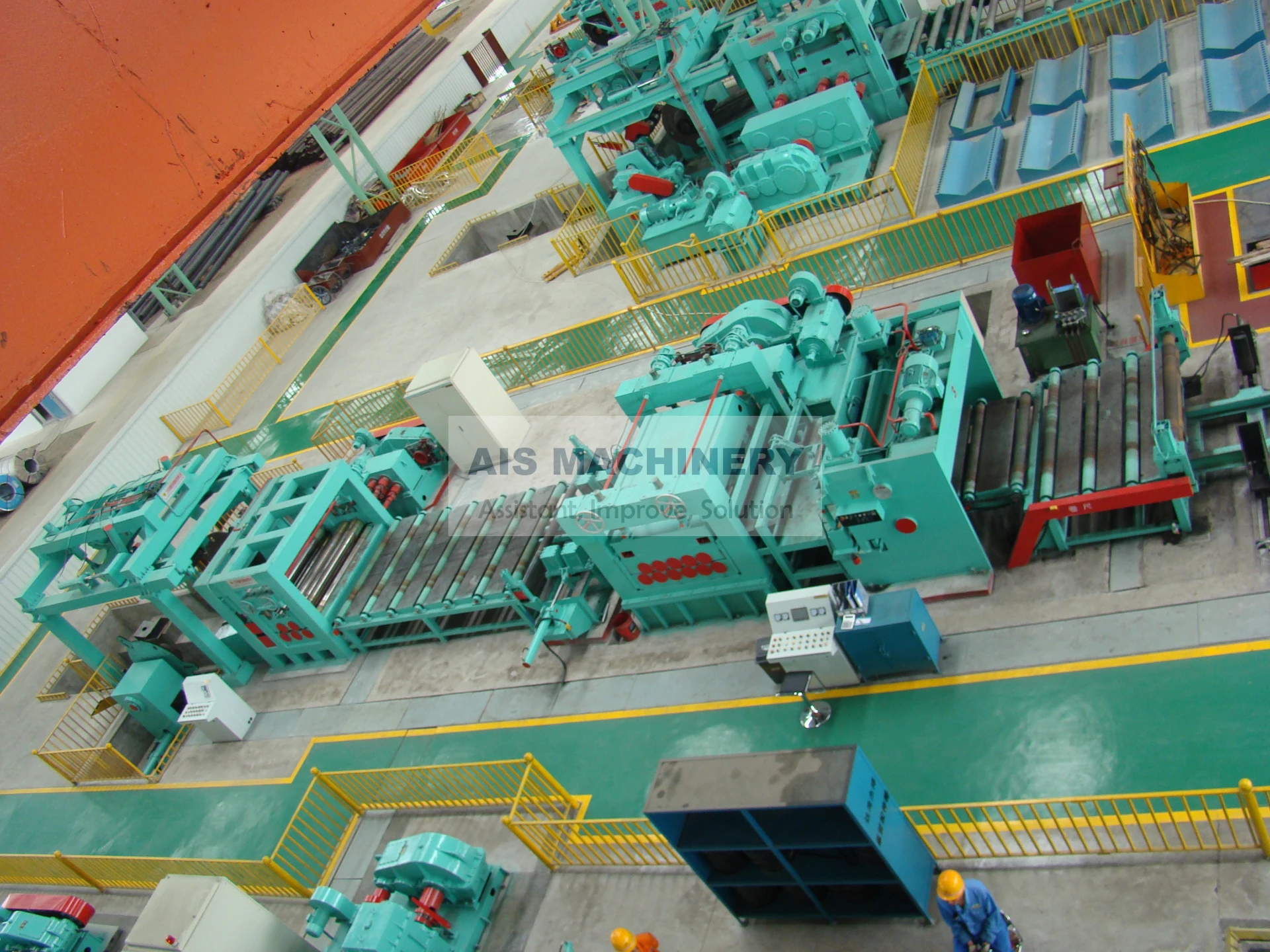

FAQS on solid state welding process
Q: What is a solid state welding process?
Q: What are key applications of solid state welding?
Q: What are the main types of solid state welding?
Q: How does friction welding work in solid state processes?
Q: Why choose solid state welding over other methods?
Related Products
Related News
Send a Message
Dear customer, thank you for your attention! We provide high-quality machinery and equipment and look forward to your orders. Please inform us of your needs and we will respond quickly!