-
 Tel:86-15176910262
Tel:86-15176910262
-

Search


what is a erw tube mill
3월 . 07, 2025 01:52
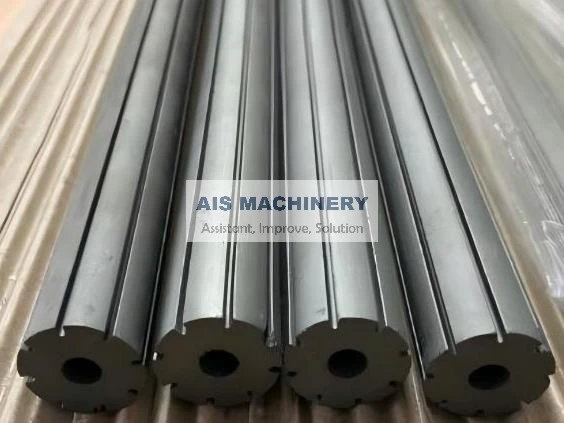
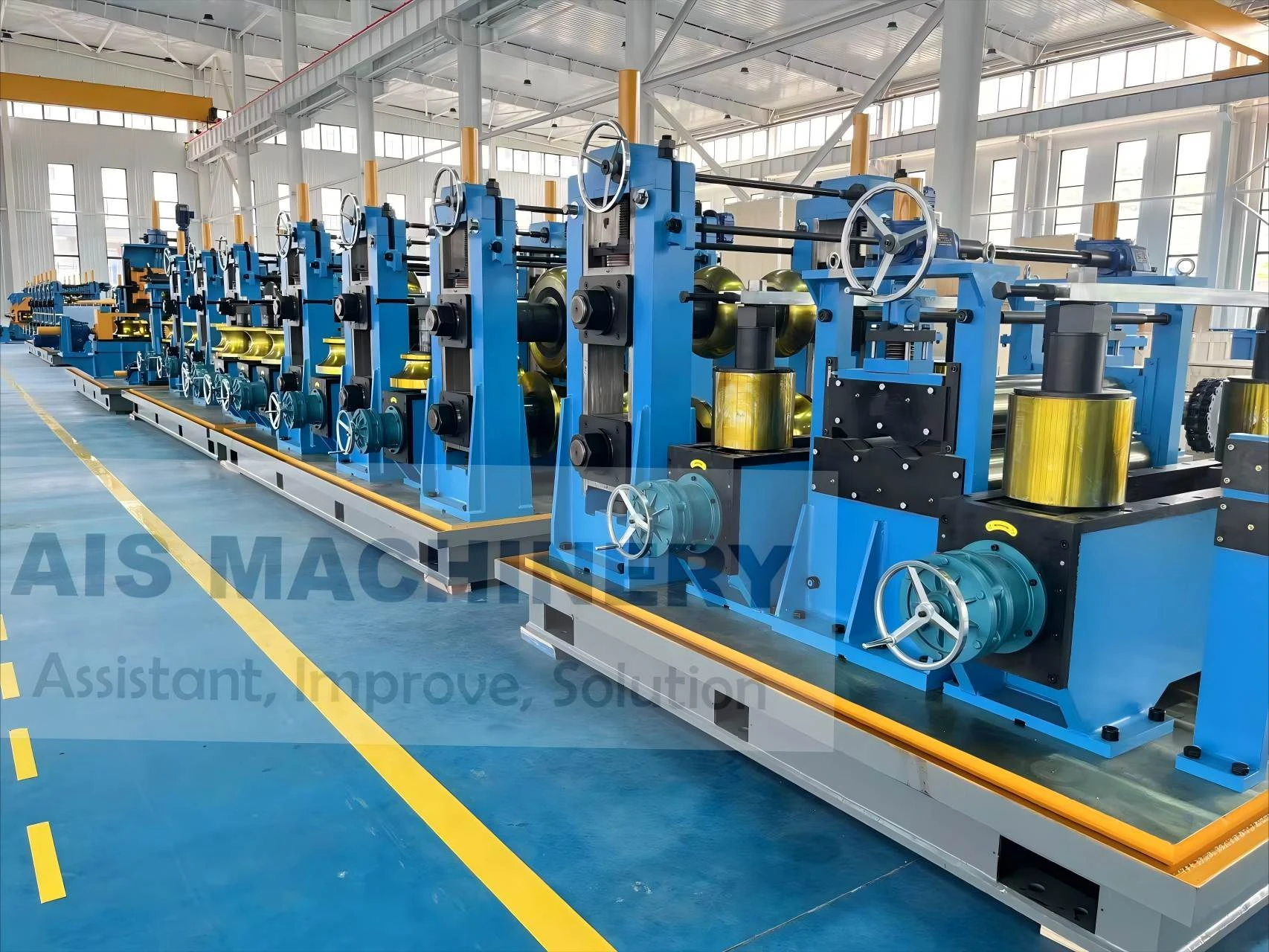
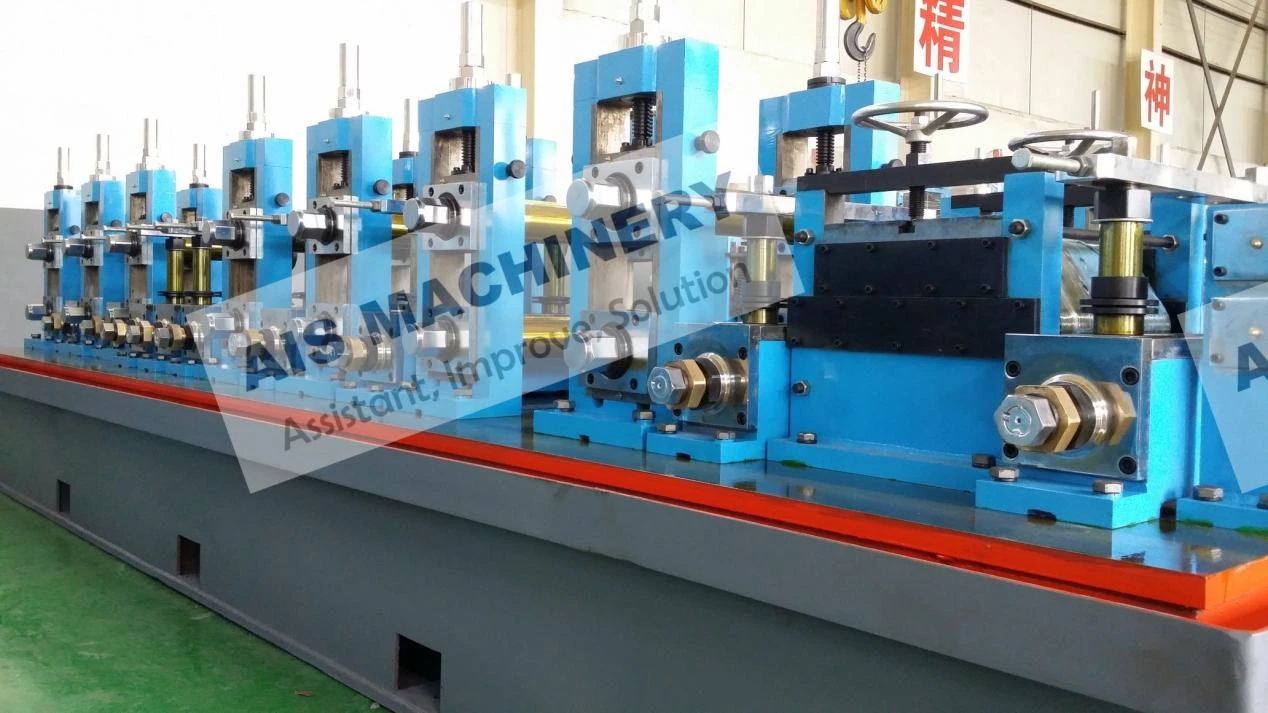
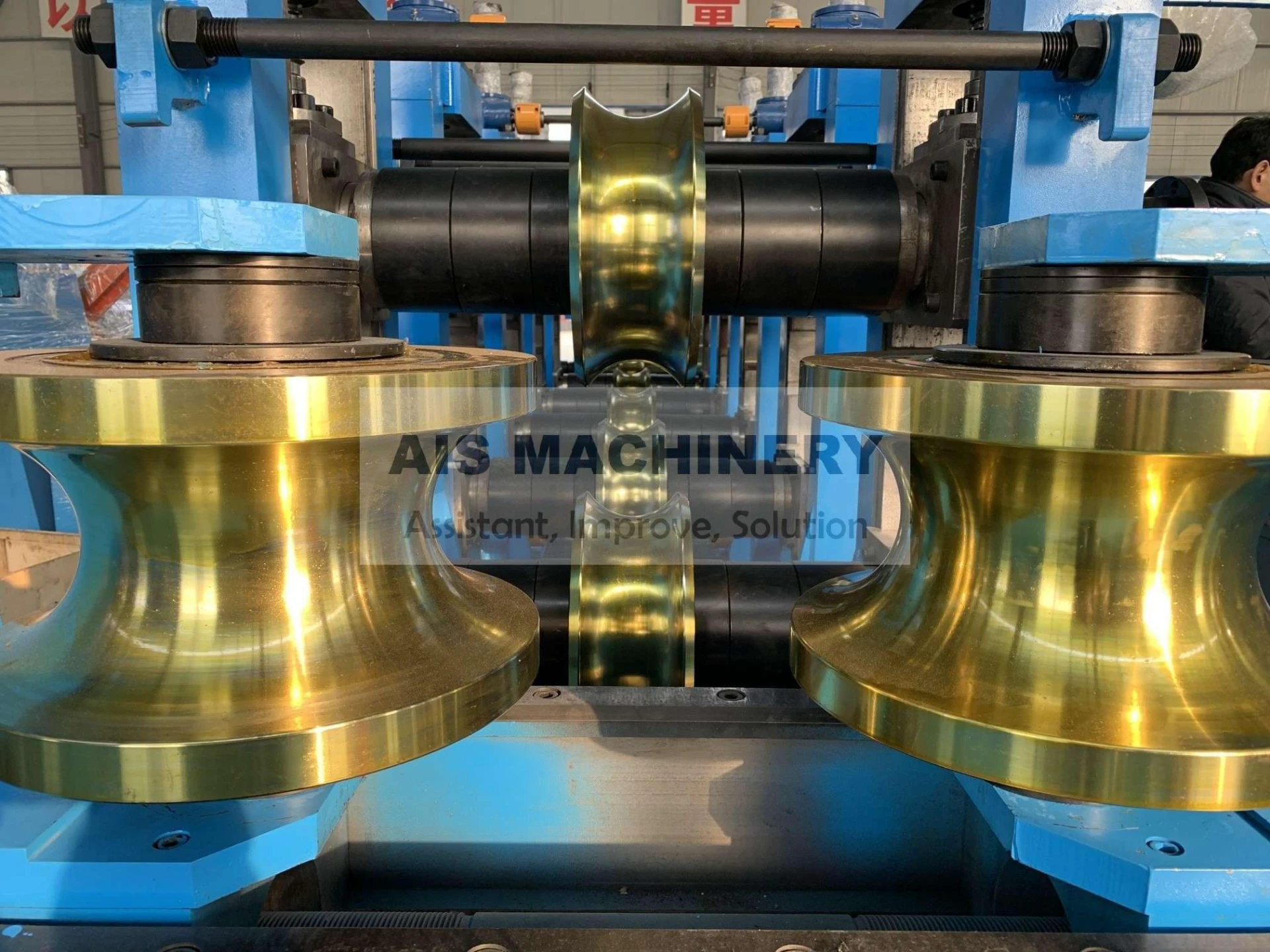
In the realm of industrial manufacturing, the ERW tube mill stands out as a pivotal innovation in the production of welded pipes. Its relevance spans several industries, including construction, automotive, and infrastructure. This article will delve deep into the workings, applications, and benefits of an Electric Resistance Welding (ERW) tube mill, emphasizing its significance and efficiency.
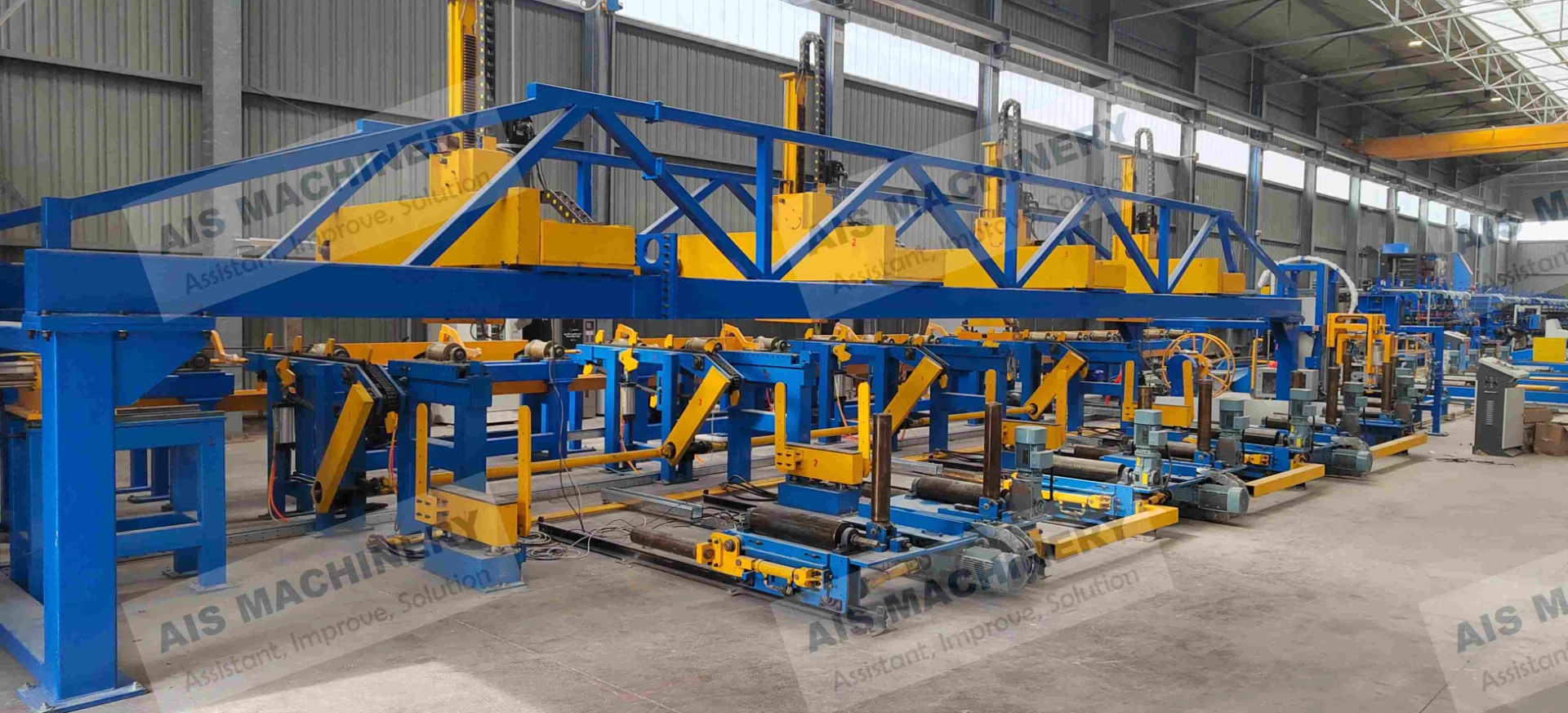
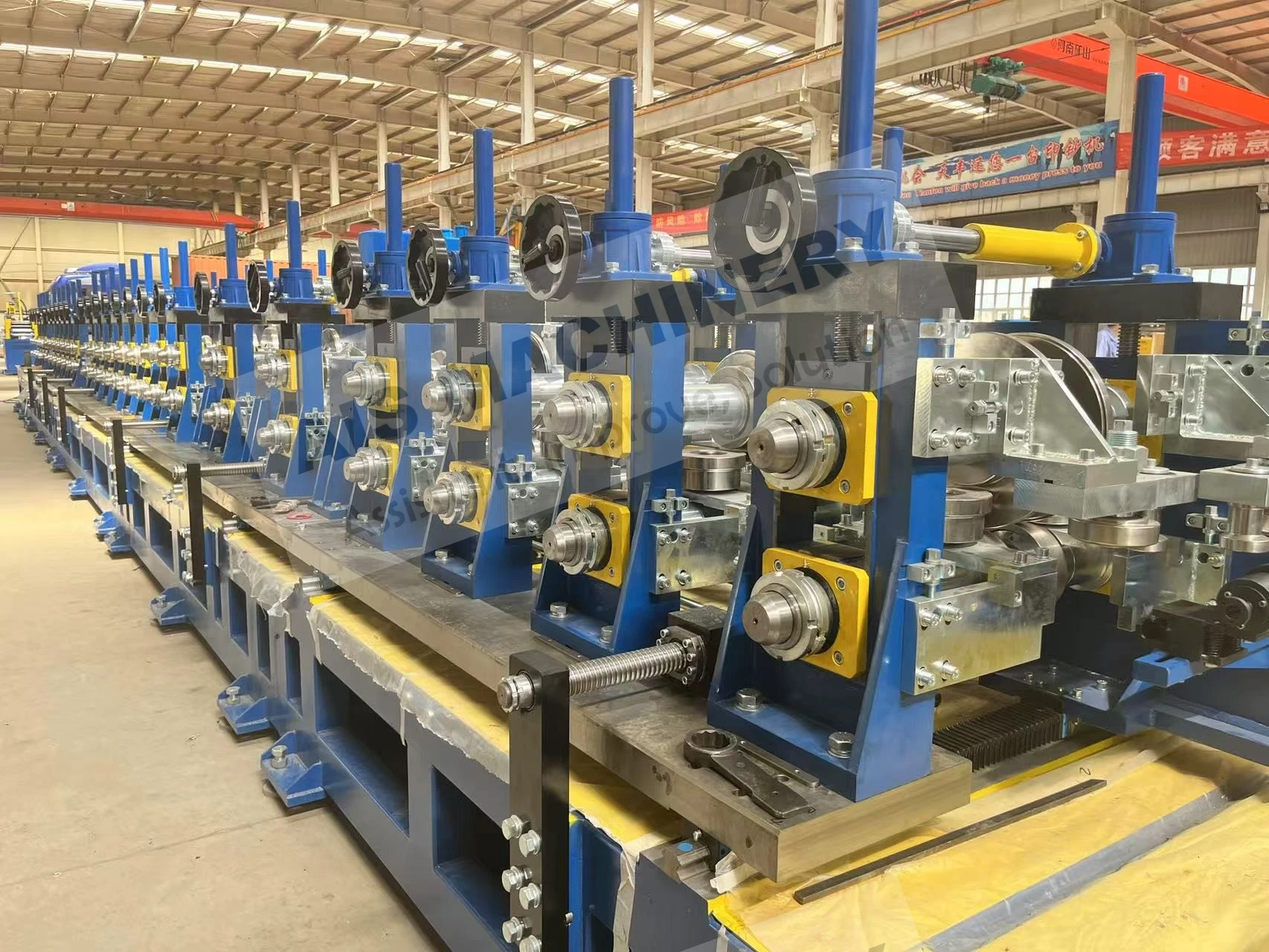
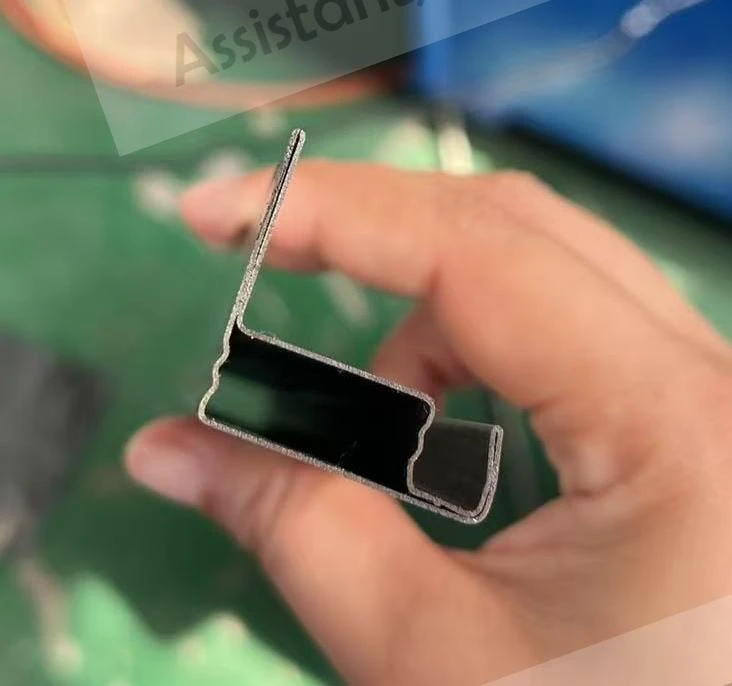
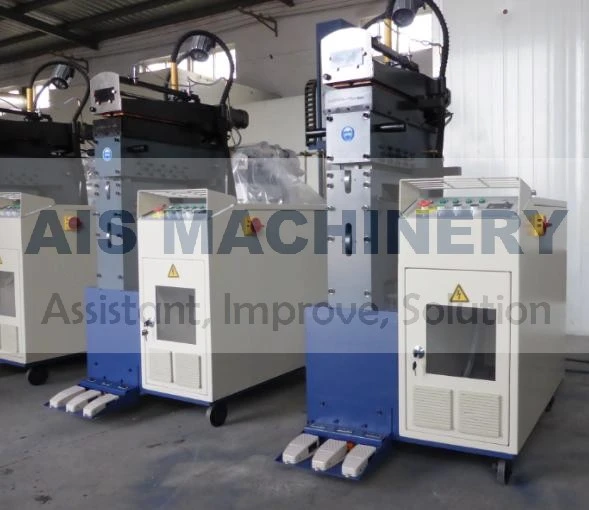
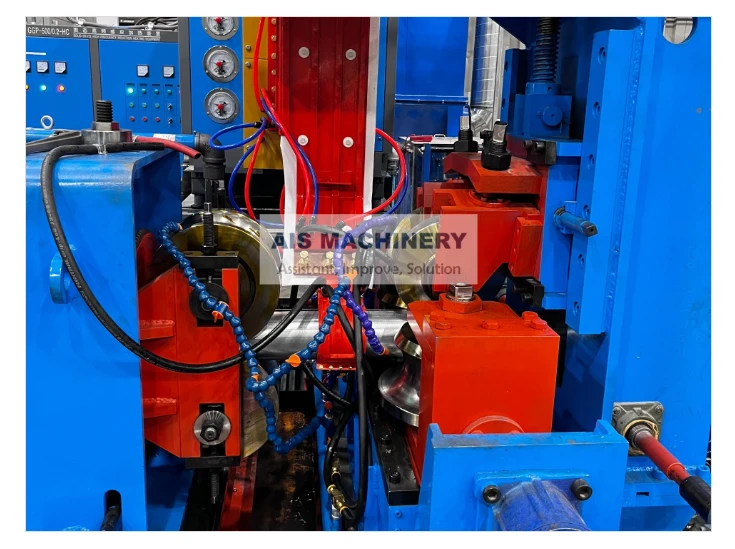
One of the foremost benefits of an ERW tube mill is its efficiency. The continuous production process allows for high-speed output, catering to large-scale industrial demands. This efficiency is complemented by the mill's ability to produce a wide variety of tube sizes and shapes, making it adaptable to different industry requirements. The automation within modern ERW tube mills significantly enhances their productivity. Advanced models integrate computer-controlled systems that oversee every stage of the process, adjusting variables in real-time to optimize output and maintain quality. This technological integration not only increases throughput but also minimizes human error, further solidifying the reliability of ERW mills. Moreover, the ERW process is environmentally friendly. By eliminating the need for filler metals and reducing energy consumption through precision heating, the process minimizes waste production and energy expenditure. This aligns with the growing corporate responsibility towards sustainable manufacturing practices. The credibility and trustworthiness of ERW-produced tubes are underscored by their comprehensive application across industries. These tubes are utilized in infrastructure projects where durability and strength are non-negotiable. In the automotive sector, ERW tubes form essential structural components, contributing to vehicle safety and performance. Their use in construction ensures the integrity of buildings and facilities through reliable piping systems. In conclusion, the ERW tube mill exemplifies modern engineering's capacity to combine efficiency with quality. Its ability to produce versatile and high-strength tubes with environmental considerations positions it as a cornerstone of both contemporary manufacturing and sustainable practices. For industry professionals, understanding the nuances of an ERW tube mill is instrumental in leveraging its capabilities to meet and exceed production goals, ultimately contributing to advancements in technology and infrastructure.


One of the foremost benefits of an ERW tube mill is its efficiency. The continuous production process allows for high-speed output, catering to large-scale industrial demands. This efficiency is complemented by the mill's ability to produce a wide variety of tube sizes and shapes, making it adaptable to different industry requirements. The automation within modern ERW tube mills significantly enhances their productivity. Advanced models integrate computer-controlled systems that oversee every stage of the process, adjusting variables in real-time to optimize output and maintain quality. This technological integration not only increases throughput but also minimizes human error, further solidifying the reliability of ERW mills. Moreover, the ERW process is environmentally friendly. By eliminating the need for filler metals and reducing energy consumption through precision heating, the process minimizes waste production and energy expenditure. This aligns with the growing corporate responsibility towards sustainable manufacturing practices. The credibility and trustworthiness of ERW-produced tubes are underscored by their comprehensive application across industries. These tubes are utilized in infrastructure projects where durability and strength are non-negotiable. In the automotive sector, ERW tubes form essential structural components, contributing to vehicle safety and performance. Their use in construction ensures the integrity of buildings and facilities through reliable piping systems. In conclusion, the ERW tube mill exemplifies modern engineering's capacity to combine efficiency with quality. Its ability to produce versatile and high-strength tubes with environmental considerations positions it as a cornerstone of both contemporary manufacturing and sustainable practices. For industry professionals, understanding the nuances of an ERW tube mill is instrumental in leveraging its capabilities to meet and exceed production goals, ultimately contributing to advancements in technology and infrastructure.
Related Products
Related News
Send a Message
Dear customer, thank you for your attention! We provide high-quality machinery and equipment and look forward to your orders. Please inform us of your needs and we will respond quickly!